109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

外排泵用于抑制脓肿分枝杆菌临床分离株对克拉霉素的固有耐药性
Authors Guo Q, Chen J, Zhang S, Zou Y, Zhang Y, Huang D, Zhang Z, Li B, Chu H
Received 24 November 2019
Accepted for publication 1 February 2020
Published 12 February 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 447—454
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S239850
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eric Nulens
Purpose: The emergence of clarithromycin resistance is a challenge in treating Mycobacterium abscessus infections. Known mechanisms that contribute to intrinsic clarithromycin resistance focus on rrl gene-related mutations, but resistant clinical isolates often exhibit an inconsistent rrl genotype.
Patients and Methods: In this study, 194 clinical Mycobacterium abscessus isolates were collected from patients with lung infections and the whole genome of each isolate was sequenced. A comprehensive examination of the molecular mechanisms underlying intrinsic clarithromycin resistance was performed, combining MIC determination, comparative genome sequence analysis and qRT-PCR.
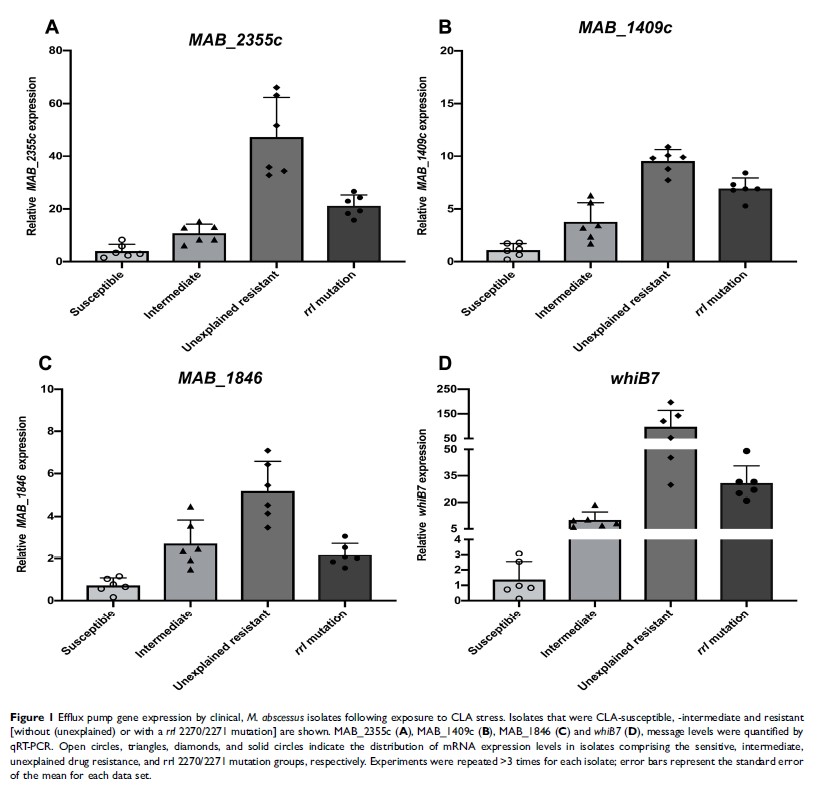
Results: Of the 194 isolates, 13 (6.7%) were clarithromycin resistant; only seven of these harbored a rrl 2270/2271 mutation. The remaining six resistant isolates did not exhibit a specific resistance-associated mutation in the clarithromycin target-site genes, rrl, rplC, rplD and rplV , or in the rrl modification gene erm(41). qRT-PCR analysis showed that the increased expression of the efflux pump genes, MAB_2355c, MAB_1409c and MAB_1846, as well as their positive regulatory gene whiB7 , consistently correlated with increased clarithromycin resistance. The presence of efflux pump inhibitors significantly decreased the MIC of clarithromycin for nonsusceptible isolates, especially the intrinsic resistant isolates that exhibited no rrl 2270/2271 mutation.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that efflux pumps play a prominent role in the intrinsic resistance of M. abscessus to clarithromycin, complementing other known resistance mechanisms.
Keywords: Mycobacterium abscessus , clarithromycin resistance, efflux pumps