109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-125b 在癌症中的新兴作用
Authors Wang Y, Zeng G, Jiang Y
Received 25 September 2019
Accepted for publication 2 February 2020
Published 12 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1079—1088
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S232388
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
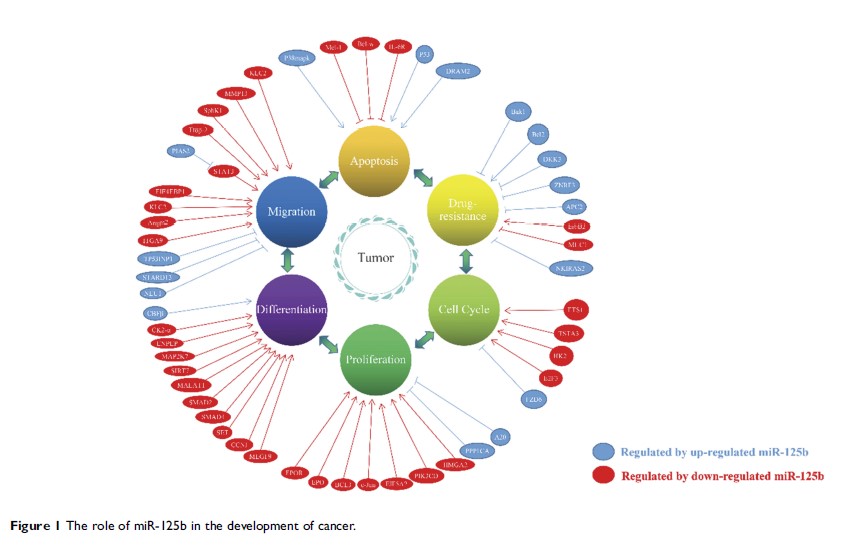
Abstract: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous, noncoding, single-stranded RNA molecules of 22 nucleotides in length. MiRNAs have both tumor-suppressive properties and oncogenic properties that can control critical processes in tumors. Mature miR-125b originates from miR-125b-1 and miR-125b-2 and leads to the degradation of target mRNAs or the inhibition of translation through binding to the 3′ untranslated regions (3′-UTR) of target mRNAs. Importantly, miR-125b is involved in regulating NF-κB, p53, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, ErbB2, Wnt, and another signaling pathways, thereby controlling cell proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, apoptosis, drug resistance and tumor immunity. This review aims to summarize the recent literature on the role of miR-125b in the regulation of tumorigenesis and to explore its potential clinical application in the diagnosis, prognosis and clinical treatment of tumors.
Keywords: miR-125b, cancer, biomarker, pathway