109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

每日一次吸入芜地溴铵 (Umeclidinium)/维兰特罗 (vilanterol) 吸入剂对亚洲 COPD 患者的疗效和安全性:来自一项随机、安慰剂对照研究的结果
Authors Zheng JP, Zhong NS, Newlands A, Church A, Goh AH
Received 17 January 2015
Accepted for publication 11 May 2015
Published 2 September 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 1753—1767
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S81053
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Background: Combination of the inhaled long-acting muscarinic antagonist umeclidinium (UMEC; GSK573719) with the long-acting β2-agonist vilanterol (VI) is an approved maintenance treatment for COPD in the US and EU. We compared the efficacy and safety of UMEC/VI with placebo in patients with COPD of Asian ancestry.
Patients and methods: In this 24-week, Phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study, patients were randomized 1:1:1 to UMEC/VI 125/25 µg, UMEC/VI 62.5/25 µg, or placebo. The primary efficacy end point was trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) on day 169; secondary end points were Transition Dyspnea Index (TDI) focal score at week 24 and weighted mean (WM) FEV1 over 0–6 hours postdose on day 1. Additional end points and safety were also assessed.
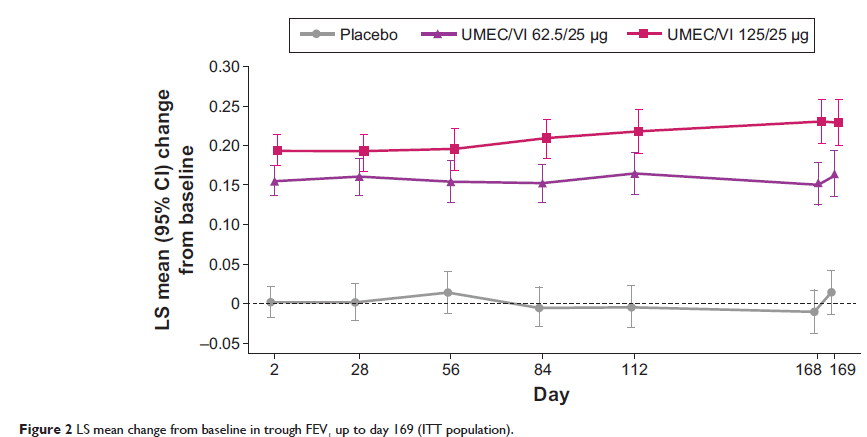
Results: Both UMEC/VI 125/25 µg and UMEC/VI 62.5/25 mg statistically significantly improved trough FEV1 at day 169 versus placebo (UMEC/VI 125/25 µg, 0.216 L, [95% confidence interval [CI] 0.175–0.257]; UMEC/VI 62.5/25 µg, 0.151 L, 95% CI 0.110–0.191; both P <0.001). Statistically significant improvements in TDI score were observed for both UMEC/VI groups versus placebo (UMEC/VI 125/25 µg, 0.9, 95% CI 0.3–1.4, P =0.002; UMEC/VI 62.5/25 µg, 0.7, 95% CI 0.1–1.2, P =0.016). On day 1, both UMEC/VI groups improved 0–6-hour WM FEV1 versus placebo (UMEC/VI 125/25 µg, 0.182 L 95% CI 0.161–0.203; UMEC/VI 62.5/25 µg, 0.160 L, 95% CI 0.139–0.181; both P <0.001). Statistically significant improvements for UMEC/VI groups versus placebo were observed for rescue albuterol use at weeks 1–24 (puffs/day, both P <0.001). The incidence of adverse events was similar across groups.
Conclusion: In Asian patients with COPD, once-daily UMEC/VI 125/25 µg and UMEC 62.5/25 µg resulted in clinically meaningful and statistically significant improvements in lung-function end points versus placebo. Symptomatic and quality of life measures also improved. The safety profile of UMEC/VI was consistent with previous studies.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, umeclidinium, vilanterol, Asian