109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
新型雄黄 (Realgar) 量子点通过内质网应激的信号通路诱发人类子宫内膜癌细胞凋亡和坏死
Authors Wang H, Liu Z, Gou Y, Qin Y, Xu Y, Liu J, Wu JZ
Received 3 March 2015
Accepted for publication 18 May 2015
Published 31 August 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5505—5512
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S83838
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
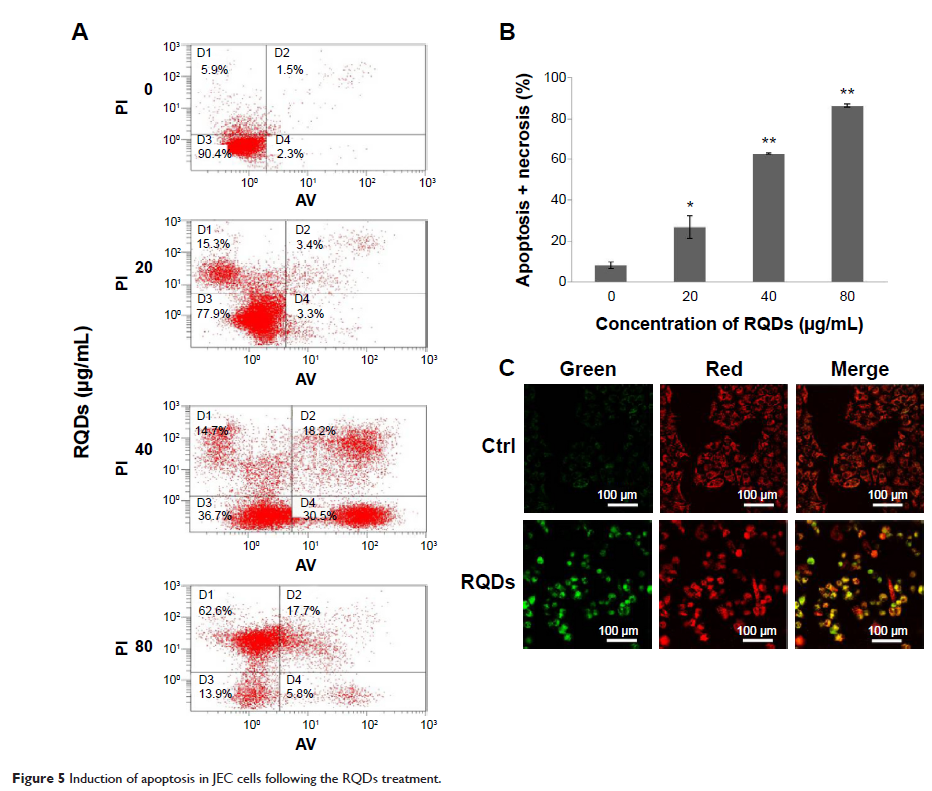
Abstract: Realgar (AS4S4) has been used in traditional medicines for malignancy, but the poor water solubility is still a major hindrance to its clinical use. Realgar quantum dots (RQDs) were therefore synthesized with improved water solubility and bioavailability. Human endometrial cancer JEC cells were exposed to various concentrations of RQDs to evaluate their anticancer effects and to explore mechanisms by the MTT assay, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), flow cytometry, real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot analysis. Results revealed that the highest photoluminescence quantum yield of the prepared RQDs was up to approximately 70%, with the average size of 5.48 nm. RQDs induced antiproliferative activity against JEC cells in a concentration-dependent manner. In light microscopy and TEM examinations, RQDs induced vacuolization and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) dilation in JEC cells in a concentration-dependent manner. ER stress by RQDs were further confirmed by increased expression of GADD153 and GRP78 at both mRNA and protein levels. ER stress further led to JEC cell apoptosis and necrosis, as evidenced by flow cytometry and mitochondrial membrane potential detection. Our findings demonstrated that the newly synthesized RQDs were effective against human endometrial cancer cells. The underlying mechanism appears to be, at least partly, due to ER stress leading to apoptotic cell death and necrosis.
Keywords: realgar, quantum dots, apoptosis, necrosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress, endometrial cancer cells
Keywords: realgar, quantum dots, apoptosis, necrosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress, endometrial cancer cells