109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
气管、支气管异物患儿- 中国西北地区 2,000 病例的回顾性研究
Authors Liang JM, Hu J, Chang HM, Gao Y, Luo HN, Wang ZH, Zheng GX, Chen F, Wang T, Yang YY, Kou XH, Xu M
Received 14 April 2015
Accepted for publication 24 June 2015
Published 28 August 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1291—1295
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S86595
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
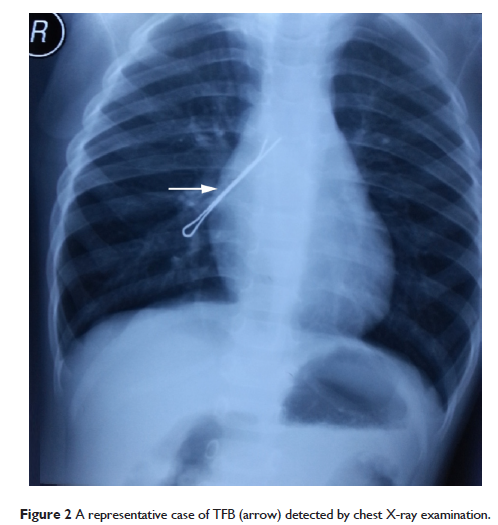
Abstract: The aim of this study is to report our experience in the diagnosis and treatment of tracheobronchial foreign bodies (TFBs). We retrospectively reviewed medical records of 2,000 TFB patients (1,260 males and 740 females) who were treated between January 2010 and December 2013. Chest radiography and computed tomography were performed to diagnose TFBs. The location and type of foreign bodies (FBs), anesthesia methods, and treatment outcomes and complications were analyzed. Overall, 72.5% of our patients with TFB were aged between 1 years and 3 years. Plant-based FBs are the most common FB type, accounting for 91.5%. Almost 52.1% of the FBs were encountered in the right bronchus. The coincidence rate for computed tomography-based three-dimensional reconstruction was significantly greater than that for chest X-ray examination (98.7% vs 82.0%, P <0.01). Under general anesthesia, the FBs were removed by rigid bronchoscopy. Neither anesthesia complication nor intraoperative hypoxemia occurred. There were seven deaths from acute obstructive asphyxia and eight from residual FB-induced chronic asphyxia and respiration-circulation failure. In conclusion, early diagnosis and prompt treatment of TFBs with rigid bronchoscopy under general anesthesia is effective in reducing complications and mortality in affected children.
Keywords: respiratory tract foreign body, children, diagnosis, treatment
Keywords: respiratory tract foreign body, children, diagnosis, treatment