109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
加载姜黄素 (Curcumin)、表面带有甘草次 (glycyrrhetinic) 酸官能化的白蛋白纳米粒子的合成、特性和体外评价
Authors Li J, Chen T, Deng F, Wan J, Tang Y, Yuan P, Zhang L
Received 9 May 2015
Accepted for publication 16 July 2015
Published 27 August 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5475—5487
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S88253
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
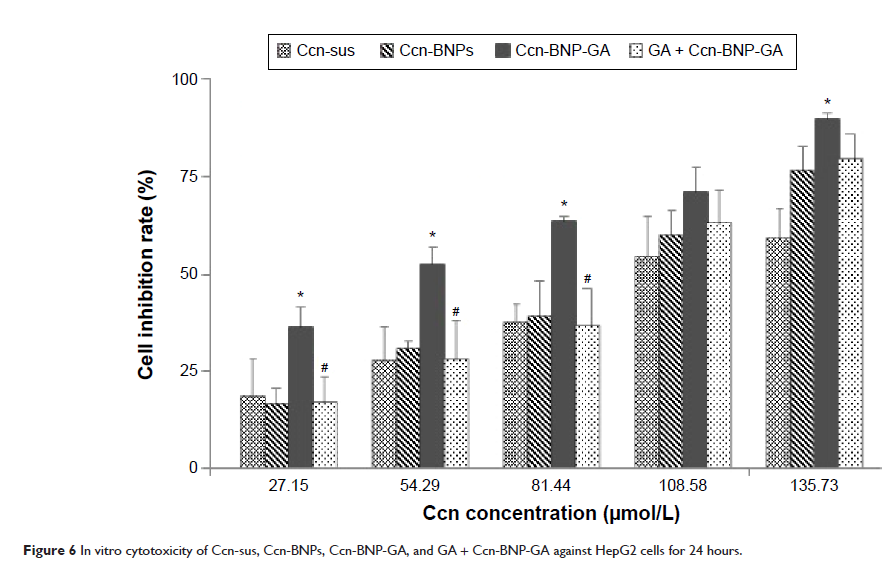
Abstract: We have designed and developed curcumin (Ccn)-loaded albumin nanoparticles (BNPs) surface-functionalized with glycyrrhetinic acid (Ccn-BNP-GA) for GA receptor-mediated targeting. Ccn-BNP-GA was prepared by conjugating GA as a hepatoma cell-specific binding molecule onto the surface of BNPs. Ccn-BNP-GA showed a narrow distribution with an average size of 258.8±6.4 nm, a regularly spherical shape, an entrapment efficiency of 88.55%±5.54%, and drug loading of 25.30%±1.58%. The density of GA as the ligand conjugated to BNPs was 140.48±2.784 µg/g bovine serum albumin. Cytotoxicity assay results indicated that Ccn-BNP-GA was significantly more cytotoxic to HepG2 cells and in a concentration-dependent manner. Ccn-BNP-GA also appeared to be taken up to a greater extent by HepG2 cells than undecorated groups, which might be due to the high affinity of GA for GA receptors on the HepG2 cell surface. These cytotoxicity assay results were corroborated by analysis of cell apoptosis and the cell cycle. Further, Ccn-BNP-GA showed an approximately twofold higher rate of cell apoptosis than the other groups. Moreover, proliferation of HepG2 cells was arrested in G2/M phase based on cell cycle analysis. These results, which were supported by the GA receptor-mediated endocytosis mechanism, indicate that BNPs surface-functionalized with GA could be used in targeted cancer treatment with high efficacy, sufficient targeting, and reduced toxicity.
Keywords: glycyrrhetinic acid, albumin, nanoparticles, surface-functionalized, curcumin
Keywords: glycyrrhetinic acid, albumin, nanoparticles, surface-functionalized, curcumin