109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
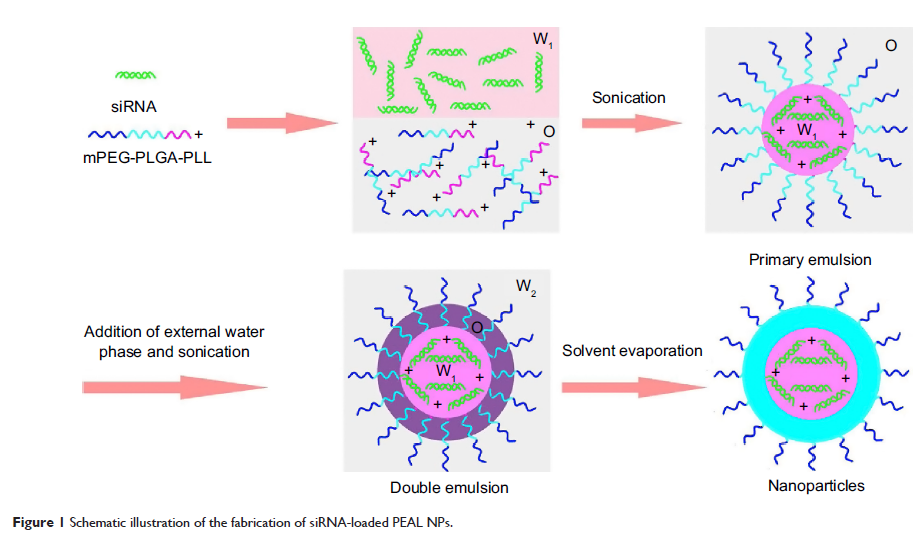
通过人类 MCF-7 / S 和 MCF-7/ ADR 细胞中的小干扰 RNA (siRNA) 转染介导体外超声靶向微泡破坏,增强了 PEAL 纳米粒子的递送
Authors Teng Y, Bai M, Sun Y, Wang Q, Li F, Xing J, Du L, Gong T, Duan Y
Received 19 January 2015
Accepted for publication 22 April 2015
Published 27 August 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5447—5457
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S81172
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: The gene knockdown activity of small interfering RNA (siRNA) has led to their use as potential therapeutics for a variety of diseases. However, successful gene therapy requires safe and efficient delivery systems. In this study, we choose mPEG-PLGA-PLL nanoparticles (PEAL NPs) with ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD) to efficiently deliver siRNA into cells. An emulsification-solvent evaporation method was used to prepare siRNA-loaded PEAL NPs. The NPs possessed an average size of 132.6±10.3 nm (n=5), with a uniform spherical shape, and had an encapsulation efficiency (EE) of more than 98%. As demonstrated by MTT assay, neither PEAL NPs nor siRNA-loaded PEAL NPs showed cytotoxicity even at high concentrations. The results of cellular uptake showed, with the assistance of UTMD, the siRNA-loaded PEAL NPs can be effectively internalized and can subsequently release siRNA in cells. Taken together, PEAL NPs with UTMD may be highly promising for siRNA delivery, making it possible to fully exploit the potential of siRNA-based therapeutics.
Keywords: gene delivery, mPEG-PLGA-PLL, UTMD, emulsification-solvent evaporation method, orthogonal design
Keywords: gene delivery, mPEG-PLGA-PLL, UTMD, emulsification-solvent evaporation method, orthogonal design