109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
微血管侵入肝癌的过表达促进细胞增殖,并通过抑制 miR-199A 的表达来抑制肝癌的细胞凋亡
Authors Shi Y, Song Q, Yu S, Hu D, Zhuang X
Received 17 April 2015
Accepted for publication 4 July 2015
Published 27 August 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 2303—2310
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S86807
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Objectives: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) associated with microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma (MVIH) has been recently reported to act as a predictor for the poor recurrence-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after hepatectomy. However, the biological role of MVIH in the tumorigenesis of HCC is still unclear.
Methods: In the study reported here, MVIH expression levels were detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in tumor tissue of HCC patients and in HCC cells, including SMMC7721 and HepG2 cells. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by MTT
and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) methods, respectively. The model of transplantation tumor of HepG2 cells in nude mice was used to evaluate the effects of MVIH and miR-199a on HCC in vivo.
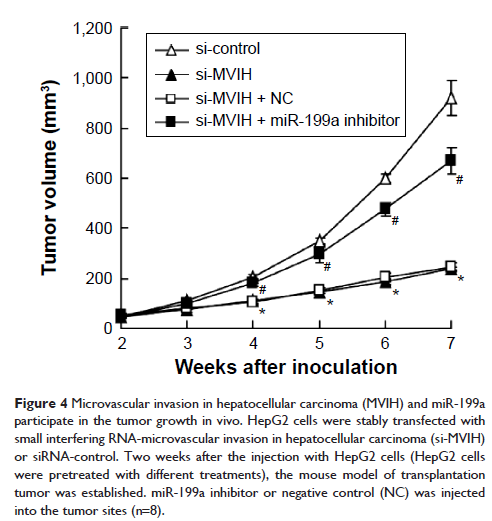
Results: MVIH expression was significantly increased and miR-199a expression was significantly decreased in tumor tissue and HCC cells. si-MVIH inhibited HCC cell viability and promoted cell apoptosis, but this effect was reversed by miR-199a inhibitor. Luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation experiment showed that miR-199a had a direct binding ability to MVIH RNA. In nude mice with transplantation, the tumor volume was reduced by si-MVIH, and miR-199a inhibitor canceled this decrease.
Conclusion: MVIH promoted cell growth and inhibited cell apoptosis of HCC via inhibiting miR-199a expression.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, HCC, miR-199a, cell apoptosis
Methods: In the study reported here, MVIH expression levels were detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in tumor tissue of HCC patients and in HCC cells, including SMMC7721 and HepG2 cells. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by MTT
and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) methods, respectively. The model of transplantation tumor of HepG2 cells in nude mice was used to evaluate the effects of MVIH and miR-199a on HCC in vivo.
Results: MVIH expression was significantly increased and miR-199a expression was significantly decreased in tumor tissue and HCC cells. si-MVIH inhibited HCC cell viability and promoted cell apoptosis, but this effect was reversed by miR-199a inhibitor. Luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation experiment showed that miR-199a had a direct binding ability to MVIH RNA. In nude mice with transplantation, the tumor volume was reduced by si-MVIH, and miR-199a inhibitor canceled this decrease.
Conclusion: MVIH promoted cell growth and inhibited cell apoptosis of HCC via inhibiting miR-199a expression.
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, HCC, miR-199a, cell apoptosis