109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA HCP5 通过 miR-140-5p/SOX4 轴促进口腔鳞状细胞癌的细胞侵袭和上皮-间质转化
Authors Zhao J, Bai X, Feng C, Shang X, Xi Y
Received 9 September 2019
Accepted for publication 25 October 2019
Published 12 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10455—10462
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S230324
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the predominant histological type of human oral cancer. In this study, we sought to investigate the functional role of lncRNA HCP5 in OSCC progression.
Methods: The HCP5 and miR-140-5p expression level was determined in 73 paired OSCC tissues and their adjacent normal tissues. Knockdown or overexpression of HCP5 was conducted to investigate the effects of HCP5 on malignant behaviors of OSCC cells. Then, bioinformatic prediction and dual-luciferase reporter assay were conducted to study the interaction between HCP5 and miR-140-5p in OSCC.
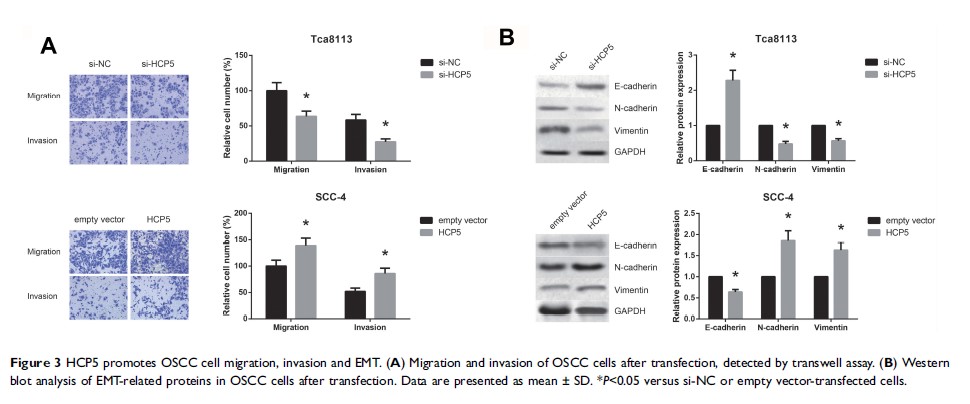
Results: Our results demonstrated that HCP5 expression was significantly increased in OSCC tissues and cell lines. High HCP5 level was associated with the aggressive clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis of OSCC patients. In vitro gain- and loss-of-function experiments showed that HCP5 overexpression promoted, whereas HCP5 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of OSCC cells. Mechanistically, we confirmed that HCP5 might serve as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-140-5p to alleviate the repression of its downstream target, SOX4, a master regulator of EMT. Furthermore, restoration of miR-140-5p expression diminished the oncogenic effects of HCP5 on OSCC cells.
Conclusion: Overall, the present study indicated that HCP5/miR-140-5p/SOX4 axis might be a ponderable and promising therapeutic target for OSCC.
Keywords: oral squamous cell carcinoma, long non-coding RNA HCP5, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, competitive endogenous RNA