109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PRPH2 激活河马信号通路并抑制喉癌的侵袭及遏制失巢凋亡
Authors Dong K, Xue H, Cheng J, Su J, Li D, Zhang J, Zhang H
Received 9 July 2019
Accepted for publication 12 November 2019
Published 2 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10107—10115
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S222527
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Introduction: Laryngeal cancer is the most common head and neck cancer worldwide. It is urgent to identify the mechanisms underlying laryngeal cancer pathogenesis. In the present study, we investigated the biological functions of Peripherin 2 (PRPH2) in laryngeal cancer and uncovered the molecular mechanism underlying this disease.
Methods: Laryngeal cancer tissues were used to analyze the expression of PRPH2. In vitro transwell matrigel invasion assay and annexin V anoikis assay in laryngeal cancer cells were conducted to investigate PRPH2 related biological functions. Quantitative real-time PCR and Western blotting were performed to investigate the expression and mechanism of PRPH2 in laryngeal cancer.
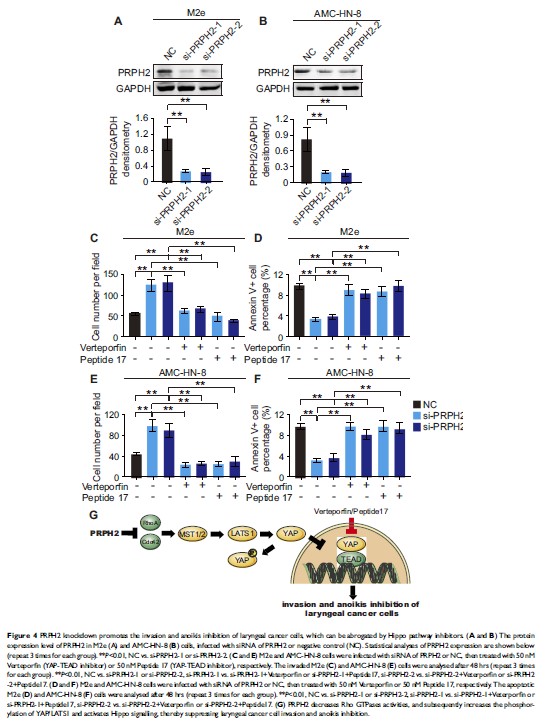
Results: We found that the expression of PRPH2 was significantly downregulated in laryngeal cancer tissues. Overexpression of PRPH2 suppressed the invasion and anoikis inhibition of laryngeal cancer cells. Furthermore, PRPH2 overexpression increased the phosphorylation of YAP and LATS1 and decreased the activities of Rho GTPases, while PRPH2 knockdown had opposite effects. Inhibitors of the Hippo pathway abrogated PRPH2 knockdown-induced laryngeal cancer cell invasion and anoikis inhibition.
Discussion: These results suggested that PRPH2 suppresses laryngeal cancer cell invasion and anoikis inhibition by activating Hippo signalling. PRPH2 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for laryngeal cancer in the future.
Keywords: PRPH2, hippo signaling, laryngeal cancer, invasion, anoikis inhibition