108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

术前胆红素水平可预测肝门部胆管癌患者切除后的总体生存率和肿瘤复发
Authors Li CX, Zhang H, Wang K, Wang X, Li XC
Received 11 September 2019
Accepted for publication 21 November 2019
Published 2 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10157—10165
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S230620
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Sushma Chaurasia
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
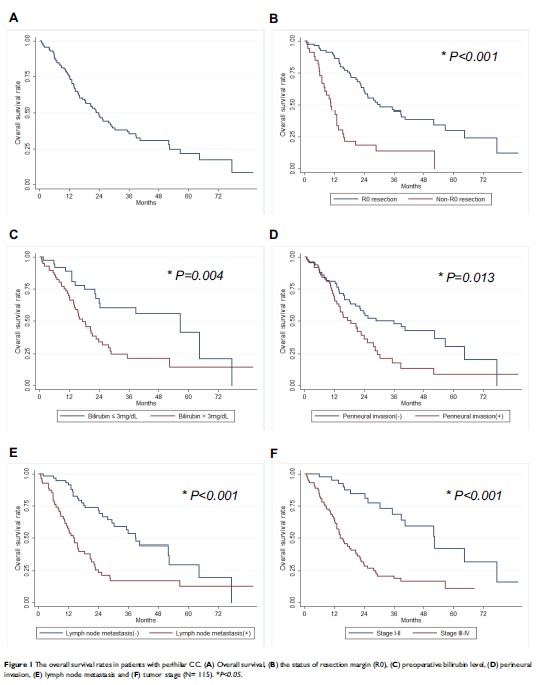
Objective: Currently, the correlation between preoperative bilirubin level and overall survival (OS) remains poorly defined in respectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (CC). The objectives of the current study were to evaluate the outcomes of perihilar CC after resection and then to analyze factors influencing curative resection, tumor recurrence and OS.
Methods: 115 patients with perihilar CC underwent surgical resection were retrospectively analyzed based on clinic characteristics, operative details, tumor recurrence and long-term survival data.
Results: The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates after resection were 75.9%, 36.5%, 21.7%, whereas the corresponding tumor recurrence rates were 29.6%, 70.8%, 85.3%, respectively. Preoperative bilirubin level combined with liver resection, resection margin, vascular invasion and perineural invasion, lymph node metastasis and TNM stage were found to be correlated with OS and tumor recurrence. Multivariate analysis showed that preoperative bilirubin level together with resection margin, perineural invasion, and TNM stage were independent predictors of OS and tumor recurrence. Furthermore, preoperative bilirubin level was related with R0 resection, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and postoperative liver function recovery.
Conclusion: Preoperative bilirubin level may effectively reflect the severity of perihilar CC and predict the OS and tumor recurrence after resection for perihilar CC patients.
Keywords: perihilar cholangiocarcinoma, surgical outcomes, predicting factors, bilirubin level, R0 resection