109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
一种有效给药系统用于新城疫病毒 DNA 疫苗的脱乙酰壳多糖包衣聚(乳酸–共轭-乙醇酸)纳米颗粒
Authors Zhao K, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Shi C, Wang X, Wang X, Jin Z, Cui S
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 4609—4619
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S70633
Received 4 July 2014, Accepted 24 July 2014, Published 30 September 2014
Approved for publication by Professor Thomas J. Webster
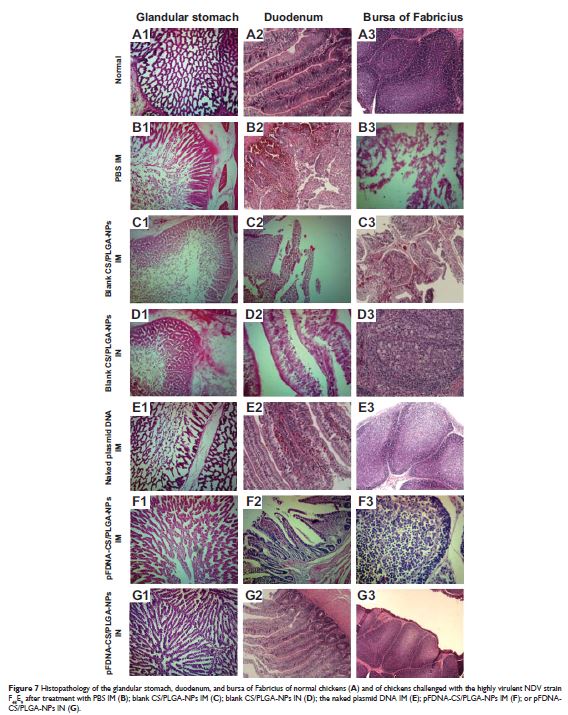
Abstract: We determined the efficacy and safety of chitosan (CS)-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles (NPs) as a delivery system for a vaccine to protect chickens against Newcastle disease virus (NDV). The newly constructed vaccine contained DNA (the F gene) of NDV. The Newcastle disease virus (NDV) F gene deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) plasmid (pFDNA)-CS/PLGA-NPs were spherical (diameter =699.1±5.21 nm [mean ± standard deviation]) and smooth, with an encapsulation efficiency of 98.1% and a Zeta potential of +6.35 mV. An in vitro release assay indicated that CS controlled the burst release of plasmid DNA, such that up to 67.4% of the entire quantity of plasmid DNA was steadily released from the pFDNA-CS/PLGA-NPs. An in vitro expression assay indicated that the expression of nanoparticles (NPs) was maintained in the NPs. In an immunization test with specific pathogen-free chickens, the pFDNA-CS/PLGA-NPs induced stronger cellular, humoral, and mucosal immune responses than the plasmid DNA vaccine alone. The pFDNA-CS/PLGA-NPs did not harm 293T cells in an in vitro assay and did not harm chickens in an in vivo assay. Overall, the results indicated that CS-coated PLGA NPs can serve as an efficient and safe mucosal immune delivery system for NDV DNA vaccine.
Keywords: mucosal immune delivery system, immune effect
Keywords: mucosal immune delivery system, immune effect