108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超声靶向微泡破坏介导的局部肿瘤缺血再灌注可增强阿霉素化疗的抗肿瘤功效
Authors Wu M, Song Z, Zhang S, Dan Q, Tang C, Peng C, Liang Y, Zhang L, Wang H, Li Y
Received 1 August 2019
Accepted for publication 9 October 2019
Published 5 November 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 9387—9395
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S225607
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD) has been shown to be a promising noninvasive technique to change the tumor circulation, thus providing a potential method to increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in tumors by inducing tumor tissue ischemia-reperfusion (IR). In this study, we investigated the feasibility of local tumor IR through UTMD to enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of doxorubicin (DOX) chemotherapy.
Methods: UTMD was used to induce local tumor IR. After the major blood supply of the tumor was restored, DOX was intravenously injected into the tumor-bearing mice. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activity and ROS levels were examined, and the anti-tumor efficacy was evaluated.
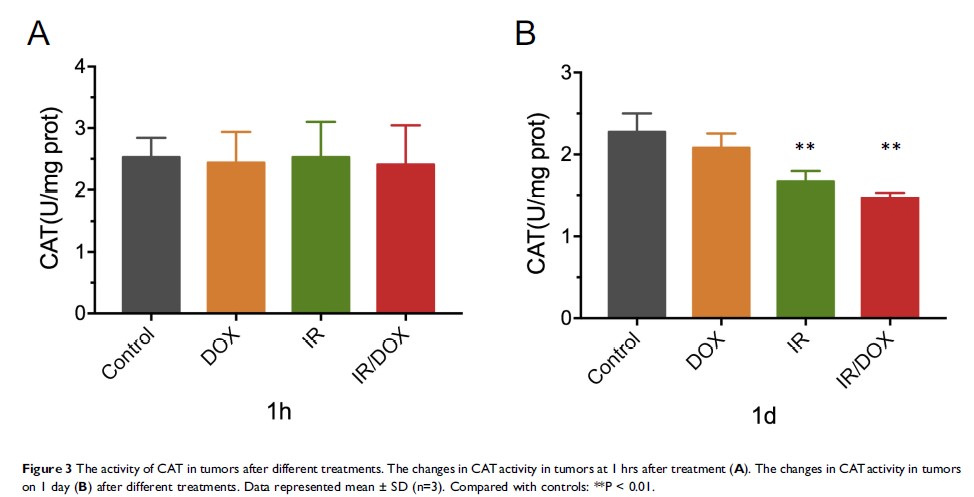
Results: UTMD blocked the circulation to the tumor for 30 mins. Slow reperfusion began to occur after 30 mins, and major blood supply was restored after 1 hr. The blood perfusion of the tumor completely recovered at 2 hrs. The activity of SOD in the tumors was significantly decreased at 2 hrs and 1 day after IR treatment with or without DOX treatment. The CAT activity showed no obvious changes at 2 hrs after IR treatment, whereas a significant decrease was found after 1 day in both the IR and DOX/IR groups. Moreover, higher levels of ROS were produced in the IR group and IR/DOX group. In vivo anti-tumor study indicated that the local tumor IR strategy may significantly enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of DOX chemotherapy.
Conclusion: UTMD provides a novel, simple and non-invasive technique for tumor IR. In combination with chemotherapy, UTMD may have high great potential to improve the anti-tumor efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Keywords: ischemia-reperfusion, ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction, breast tumor, doxorubicin, combined treatment