109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
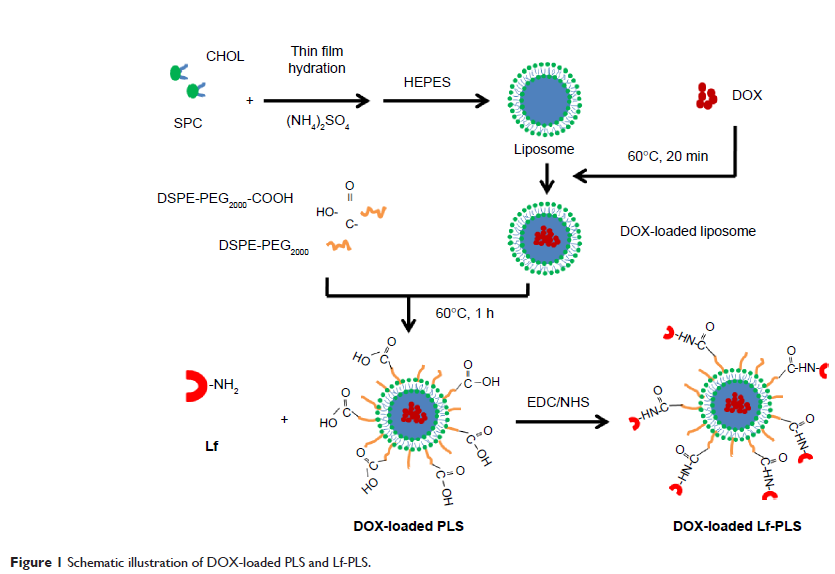
装载阿霉素 (Doxorubicin) 和以乳铁蛋白 (Lactoferrin) 修饰的聚乙二醇 (PEG) 化脂质体被用于靶向递送至肝细胞癌
Authors Wei MY, Guo XC, Tu LX, Zou Q, Li Q, Tang CY, Chen B, Xu YH, Wu CB
Received 20 April 2015
Accepted for publication 7 June 2015
Published 12 August 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5123—5137
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S87011
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Lactoferrin (Lf) is a potential-targeting ligand for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells because of its specific binding with asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR). In this present work, a doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded, Lf-modified, polyethylene glycol (PEG)ylated liposome (Lf-PLS) system was developed, and its targeting effect and antitumor efficacy to HCC was also explored. The DOX-loaded Lf-PLS system had spherical or oval vesicles, with mean particle size approximately 100 nm, and had an encapsulation efficiency of 97%. The confocal microscopy and flow cytometry indicated that the cellular uptake of Lf-PLS was significantly higher than that of PEGylated liposome (PLS) in ASGPR-positive cells (P <0.05) but not in ASGPR-negative cells (P >0.05). Cytotoxicity assay by MTT demonstrated that DOX-loaded Lf-PLS showed significantly stronger antiproliferative effects on ASGPR-positive HCC cells than did PLS without the Lf modification (P <0.05). The in vivo antitumor studies on male BALB/c nude mice bearing HepG2 xenografts demonstrated that DOX-loaded Lf-PLS had significantly stronger antitumor efficacy compared with PLS (P <0.05) and free DOX (P <0.05). All these results demonstrated that a DOX-loaded Lf-PLS might have great potential application for HCC-targeting therapy.
Keywords: asialoglycoprotein receptor, immunoliposome, PEGylated modification, post-insertion, hepatic cancer, active targeting
Keywords: asialoglycoprotein receptor, immunoliposome, PEGylated modification, post-insertion, hepatic cancer, active targeting