109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
组蛋白去甲基化酶 PHF8 通过激活 oncomiR miR-125b 促进前列腺癌细胞的生长
Authors Ma Q, Chen Z, Jia G, Lu X, Xie X, Jin W
Received 25 March 2015
Accepted for publication 19 May 2015
Published 10 August 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1979—1988
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S85443
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Daniele Santini
Aims: Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most frequently diagnosed malignancy in men. However, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, we aim to research the molecular mechanisms underlying the initiation and progression of PCa.
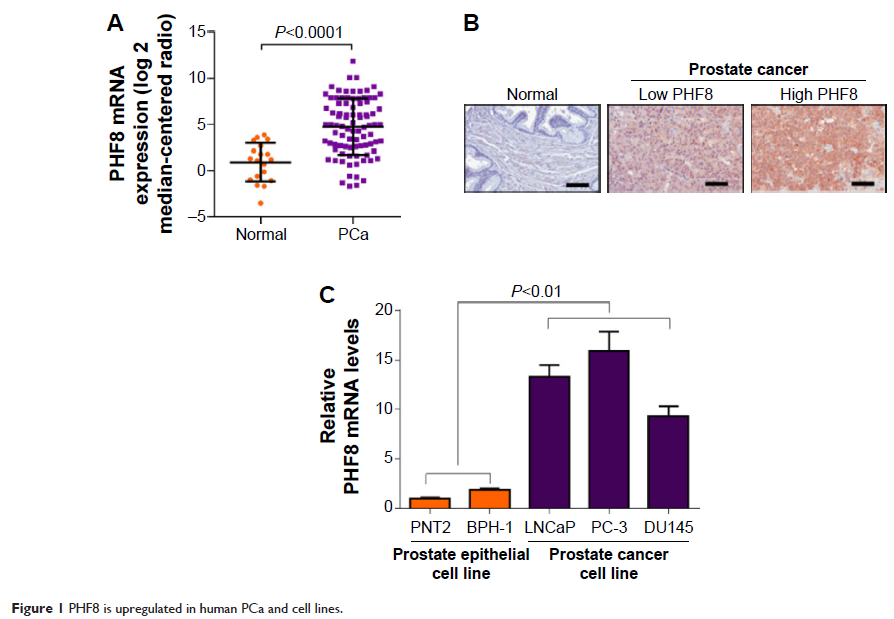
Results: Plant homeodomain finger protein 8 (PHF8) is upregulated in human PCa tissues and cell lines. PHF8 knockdown attenuates growth and cellular transformation of PCa cells. PHF8 depletion induces PCa cell apoptosis by activating proapoptotic proteins and
inactivating antiapoptotic proteins. Furthermore, miR-125b is a target of PHF8, and miR-125b seems to be essential for the hyper proliferation of PCa cells in the presence of PHF8.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we identify the histone demethylase PHF8 as an oncogenic protein in human PCa. These findings indicate PHF8 as a potential candidate for clinical intervention.
Keywords:PHF8, prostate cancer, apoptosis, miR-125b
Results: Plant homeodomain finger protein 8 (PHF8) is upregulated in human PCa tissues and cell lines. PHF8 knockdown attenuates growth and cellular transformation of PCa cells. PHF8 depletion induces PCa cell apoptosis by activating proapoptotic proteins and
inactivating antiapoptotic proteins. Furthermore, miR-125b is a target of PHF8, and miR-125b seems to be essential for the hyper proliferation of PCa cells in the presence of PHF8.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we identify the histone demethylase PHF8 as an oncogenic protein in human PCa. These findings indicate PHF8 as a potential candidate for clinical intervention.
Keywords:PHF8, prostate cancer, apoptosis, miR-125b