108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

AKAP12 内源性转录本通过直接靶向 oncomiR-183-5p 抑制大肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Hu T, Wu X, Li K, Li Y, He P, Wu Z, Fan J, Liu W, Guan M
Received 6 March 2019
Accepted for publication 15 September 2019
Published 8 October 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 8301—8310
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S207600
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jyoti Bajaj
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Purpose: Restoring lost function to suppressor gene products has captured the interest of the research community in the field of gene therapy. AKAP12 , also known as Gravin/AKAP250 , is a tumor suppressor gene, and its deregulation may be responsible for cancer progression. The aim of this study was to investigate whether AKAP12 mRNA has an anti-cancer function by regulating onco-miRNA expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells.
Methods: miRNAs targeting AKAP12 were predicted by bioinformatics analysis and further confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assays and RT-qPCR. The altered expression of microRNA was validated in early-stage CRC tumor tissues by miRseq. Cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Cell invasion and migration were detected by transwell and wound healing assays, respectively. In vivo experiments were conducted to confirm the in vitro findings.
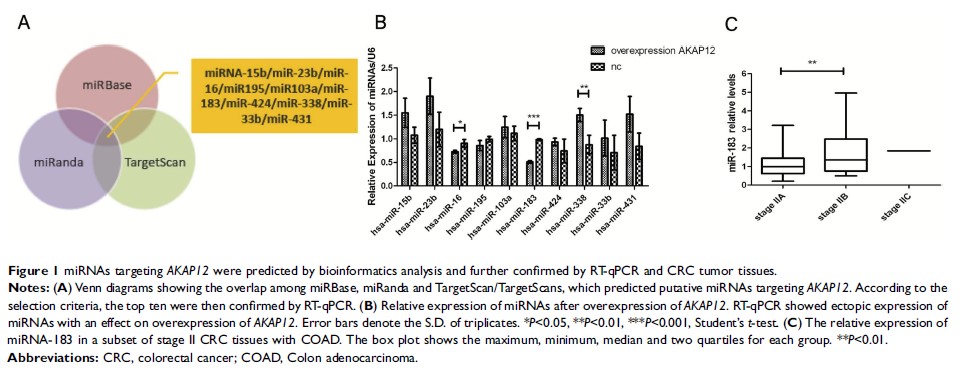
Results: Among all miRNAs, reversed correlation between AKAP12 expression and miRNA-183-5p expression was most significant. Luciferase assays revealed that AKAP12 directly targeted miR-183-5p. The miRseq data showed that miR-183 was also dysregulated at the early stage of tumor development and upregulated in late sub-stage II CRC patients (P <0.01). Mechanistic analysis both in vitro and in vivo demonstrated that anti-miR-183-5p depressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in CRC cells while miR-183-5p overexpression resulted in opposite effects.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that oncomiR-183-5p promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells. AKAP12 miRNA-binding elements (MREs) suppressed miRNA-183-5p activities. Any change in expression of AKAP12 thus affected miRNA-183-5p. This may be another anti-tumor mechanism in addition to protein-mediation that regulates tumor suppressor genes.
Keywords: microRNA, cell proliferation, cell migration, cell invasion, AKAP12 endogenous transcripts, colorectal cancer cells, oncomiR-183-5p