109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
小檗碱固体脂质纳米粒都将集中在 db / db 小鼠的肝脏并改善肝细胞脂肪变性
Authors Xue M, Zhang L, Yang M, Zhang W, Li X, Ou Z, Li Z, Liu S, Li X, Yang S
Received 13 March 2015
Accepted for publication 11 May 2015
Published 6 August 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 5049—5057
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S84565
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
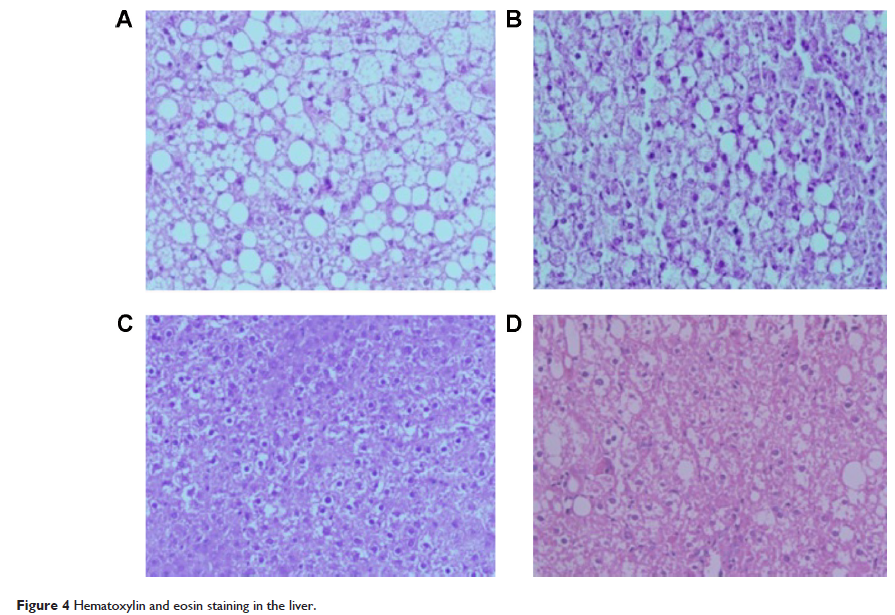
Abstract: Berberine (BBR) shows very low plasma levels after oral administration due to its poor absorption by the gastrointestinal tract. We have previously demonstrated that BBR showed increased gastrointestinal absorption and enhanced antidiabetic effects in db/db mice after being entrapped into solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). However, whether BBR-loaded SLNs (BBR-SLNs) also have beneficial effects on hepatosteatosis is not clear. We investigated the effects of BBR-SLNs on lipid metabolism in the liver using histological staining and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis. The results showed that oral administration of BBR-SLNs inhibited the increase of body weight and decreased liver weight in parallel with the reduction of serum alanine transaminase and liver triglyceride levels in db/db mice. The maximum drug concentration in the liver was 20-fold higher than that in the blood. BBR-SLNs reduced fat accumulation and lipid droplet sizes significantly in the liver, as indicated by hematoxylin and eosin and Oil Red O staining. The expression of lipogenic genes, including fatty acid synthase (FAS ), stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD1 ), and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c ) were downregulated, while lipolytic gene carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT1 ) was upregulated in BBR-SLN-treated livers. In summary, we have uncovered an unexpected effect of BBR-SLNs on hepatosteatosis treatment through the inhibition of lipogenesis and the induction of lipolysis in the liver of db/db mice.
Keywords: berberine, solid lipid nanoparticles, fatty liver, hepatosteatosis
Keywords: berberine, solid lipid nanoparticles, fatty liver, hepatosteatosis