108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

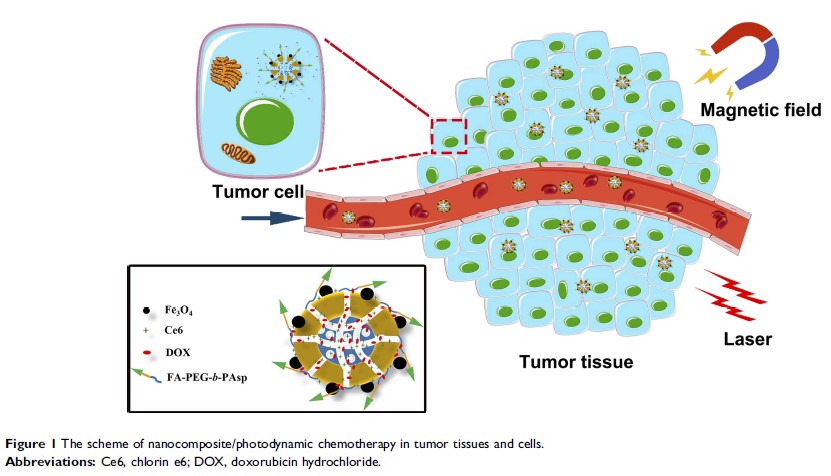
磁性和 pH 双反应纳米颗粒用于协同抗药性乳腺癌的化学/光动力疗法
Authors Wang D, Li X, Li X, Kang A, Sun L, Sun M, Yang F, Xu C
Received 3 May 2019
Accepted for publication 2 September 2019
Published 18 September 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 7665—7679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S214377
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Drug resistance is one of the prime reasons of chemotherapy failure in breast cancer and is also an important factor affecting prognosis.
Purpose: In this study, we constructed a functional magnetic mesoporous silica-based nanocomposite (MMSN) for breast cancer chemotherapy/photodynamic therapy.
Methods: MMSN was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy to observe the morphology. The size distribution and zeta potential of the MSNs were determined using Malvern Particle Size Analyzer. Anti-tumor activity in vitro was investigated by CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry and transwell experiment, and the anti-tumor activity in vivo was probed into by magnetic targeting, toxicity, and antitumor effects in breast cancer-bearing BABL/c nude mice.
Results: The results showed that the release of doxorubicin in the nanocomposites was pH sensitive, and the cumulative release rate reached 80.53% at 60 h under acidic conditions. The nanocomposites had a high cellular uptake ability in MCF-7/ADR cells, and the IC50 value of the nanocomposites on MCF-7/ADR cells was 4.23 μg/mL, much smaller than that of free DOX (363.2 μg/mL). The nanocomposites could effectively reverse resistance and induce apoptosis of MCF-7/ADR cells. The blood biochemistry parameters and H&E staining results showed no serious adverse effects after treatment with the nanocomposites. Prussian blue staining showed that the nanocomposites were able to target tumor tissues in tumor-bearing mice under a magnetic field. The combined chemical/photodynamic therapy significantly inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Nanocomposites with magnetic and pH dual-responsive performance has shown a promising platform for enhanced drug-resistant breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: magnetic mesoporous silica, doxorubicin, magnetic targeting, pH responsive, photodynamic therapy