108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FLI-06 截获 Notch 信号并抑制舌癌细胞的增殖和自我更新
Authors Gan R, Lin L, Xie J, Huang L, Ding L, Su B, Peng X, Zheng D, Lu Y
Received 29 June 2019
Accepted for publication 29 August 2019
Published 18 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7663—7674
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S221231
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Purpose: The Notch signaling pathway plays an oncogenic role in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. The aim of this study was to inhibit the proliferation and self-renewal of tongue cancer cells by applying Notch signaling pathway inhibitor FLI-06 (Selleck, USA) and to lay a foundation for the clinically targeted treatment of tongue cancer for the future.
Methods: The mRNA expression level of Notch1 and the overall survival rate of patients with tongue cancer were examined by analyzing the TCGA database. Tongue cancer cells were treated with FLI-06. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, and stem cell self-renewal ability were tested in appropriate ways. A xenograft mouse model was established to observe tumor growth.
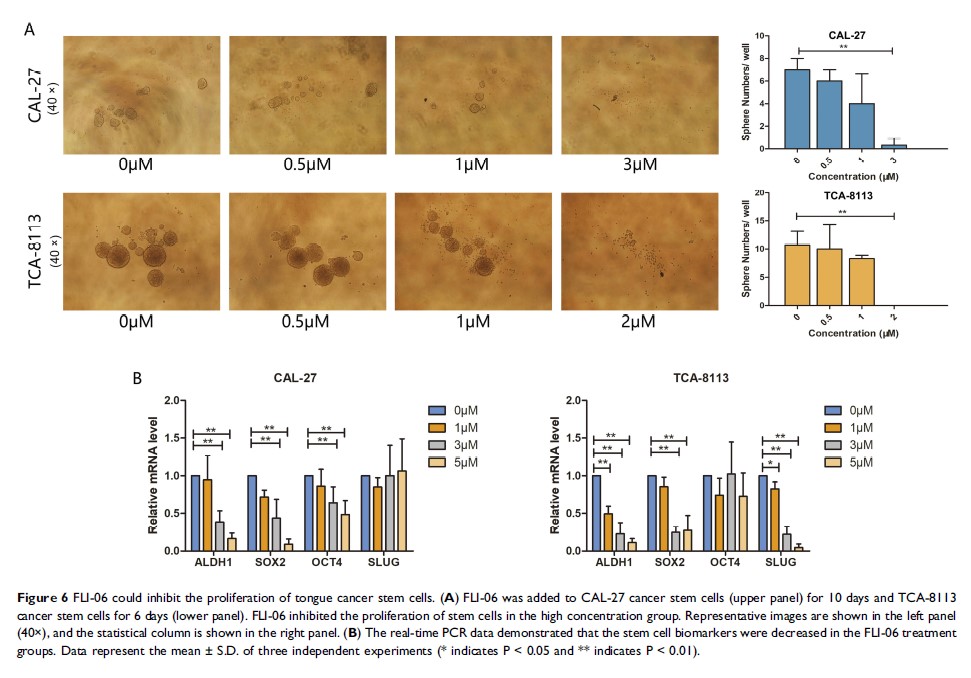
Results: From the TCGA data, we demonstrated that patients with high expression of Notch1 had a poor prognosis. We observed that the Notch signaling pathway inhibitor FLI-06 can restrain the activation of the Notch signaling pathway, decrease cell proliferation and induce cell apoptosis in vitro. The xenograft experiment indicated that intraperitoneal injection of FLI-06 inhibited tumor growth and increased cell apoptosis. FLI-06 suppressed both the mRNA and protein expression of Notch receptor and Notch targeted genes. We also observed that FLI-06 suppressed the proliferation of tongue cancer stem cells.
Conclusion: FLI-06 can block the proliferation and self-renewal of tongue cancer cells. It is inferred that this compound, which inhibits the Notch signaling pathway, may serve as a potential targeted drug for the treatment of tongue cancer in the clinic.
Keywords: tongue cancer, Notch signaling pathway, Notch inhibitor, cancer stem cells