108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大黄素通过抑制 Stat3 信号通路使人胰腺癌细胞对 EGFR 抑制剂敏感
Authors Wang Z, Chen H, Chen J, Hong Z, Liao Y, Zhang Q, Tong H
Received 4 July 2019
Accepted for publication 28 August 2019
Published 17 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8463—8473
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S221877
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Background: Excessive expression of EGFR is closely related to tumor formation, transfer and deterioration, which has attracted much attention. EGFR overexpression may be detected in up to 90% of pancreatic tumors. However, drug resistance of EGFR inhibitors targeting treatment severely limits its clinical application.
Methods: In this study, Western blotting was used to detect the expression of p-Stat3, EGFR, Bcl-2, cleaved-caspase3 and Bax. Cell apoptosis was evaluated via flow cytometry. The colon assay and MTT assay were applied for detecting the cell proliferation in vitro. The xenograft mouse model was used to examine the cell proliferation in vivo.
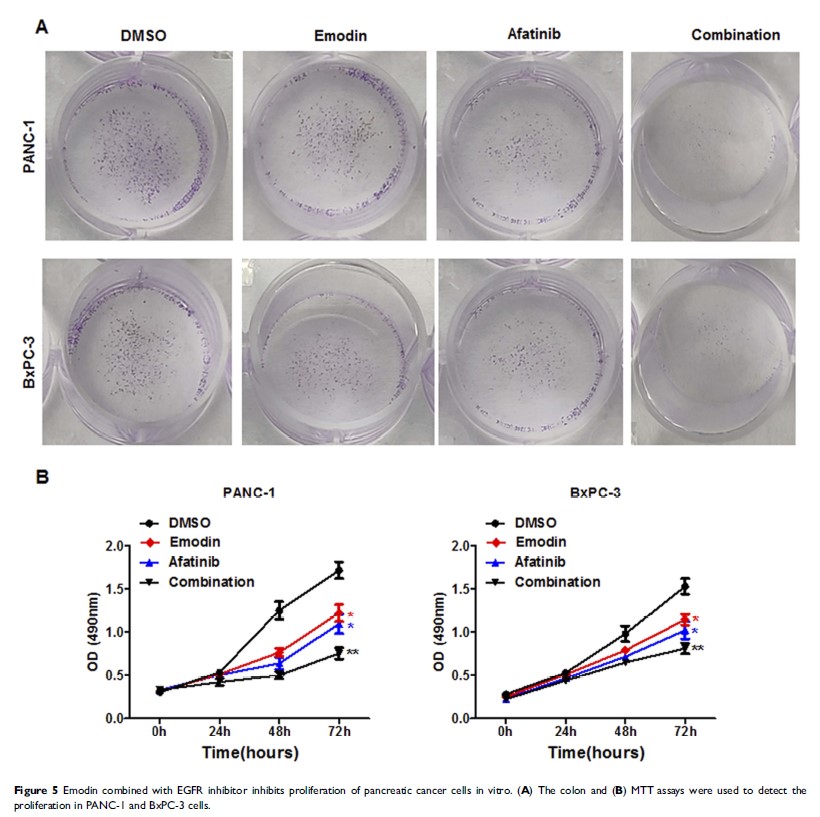
Results: Emodin remarkably enhanced the anti-cancer effect of EGFR inhibitor on pancreatic cancer cells. In addition, emodin promoted afatinib-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the Stat3 signaling pathway. Meanwhile, siRNAs against Stat3 significantly increased the apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. EGFR inhibitor promoted phosphorylation of Stat3 in pancreatic cancer cells. Interestingly, emodin combined with EGFR inhibitor inhibited the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. The tumor xenograft mice model was further confirmed that emodin possessed a synergy anticancer effect with afatinib on pancreatic cancer cells by regulating the Stat3 expression.
Conclusion: These results indicate that the combination of emodin with EGFR inhibitor is an effective therapeutic strategy to sensitize human pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, EGFR inhibitors, afatinib, Stat3