108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ACE-III 和 MoCA 检测轻度认知障碍的诊断准确性比较
Authors Wang BR, Zheng HF, Xu C, Sun Y, Zhang YD, Shi JQ
Received 15 April 2019
Accepted for publication 12 August 2019
Published 13 September 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 2647—2653
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S212328
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Objective: The aim of this study was to validate the reliability of the Chinese version of Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination III (ACE-III) for detecting mild cognitive impairment. Furthermore, the present study compares the diagnostic accuracy of ACE-III with that of Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA).
Methods: One hundred and twenty patients with MCI and 136 healthy controls were included in the study. All patients were evaluated by the Chinese version of ACE-III, MoCA and MMSE.
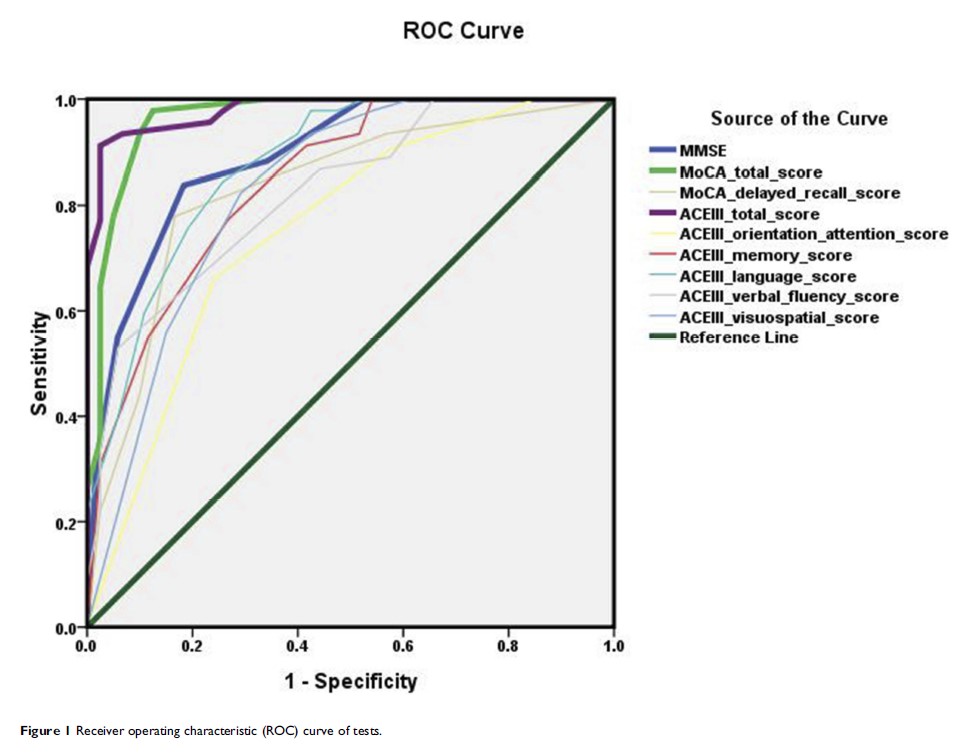
Results: Subjects in the control group showed better performance in ACE-III total score and its subdomain scores than those in the MCI group. There was a significantly positive correlation between ACE-III total score and MoCA score. Meanwhile, there was also a significantly positive correlation between ACE-III total score and MMSE score. For ACE-III total score, a cut-off point of 85 yielded a sensitivity of 97.3% and a specificity of 90.7%. The AUC for ACE-III total score was 0.978. For MoCA, a cut-off point of 23 yielded a sensitivity of 86.5% and a specificity of 97.7%. The AUC for MoCA was 0.961. There were no significant differences in diagnostic accuracy between ACE-III and MoCA.
Conclusion: The present findings support that both ACE-III and MoCA are useful for detecting MCI in early stages.
Keywords: Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination III, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, mild cognitive impairment, cognitive screening, Chinese