108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

上调的 LncRNA-ATB 通过 miR-200c 信号来调节胆管癌的生长和转移
Authors Lin H, Yang L, Tian F, Nie S, Zhou H, Liu J, Chen W
Received 30 May 2019
Accepted for publication 6 August 2019
Published 13 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7561—7571
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S217676
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Background and objective: Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly aggressive neoplasm featured with regional invasiveness and distant metastasis, which often present a phenotype of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) are dysregulated during carcinogenesis, and up-regulated LncRNA-activated by TGF-β (Lnc-ATB) supports tumor growth and metastasis via tumor suppressor microRNA 200 (miR-200). However, the role of Lnc-ATB in CCA is unclear.
Methods: CCA tissues and non-cancer tissues (n=30) were used to determine the Lnc-ATB and miR-200a/b/c levels. The functions and mechanisms of Lnc-ATB/miR-200 pathway were determined by knockdown of Lnc-ATB via siRNAs in vitro and in vivo.
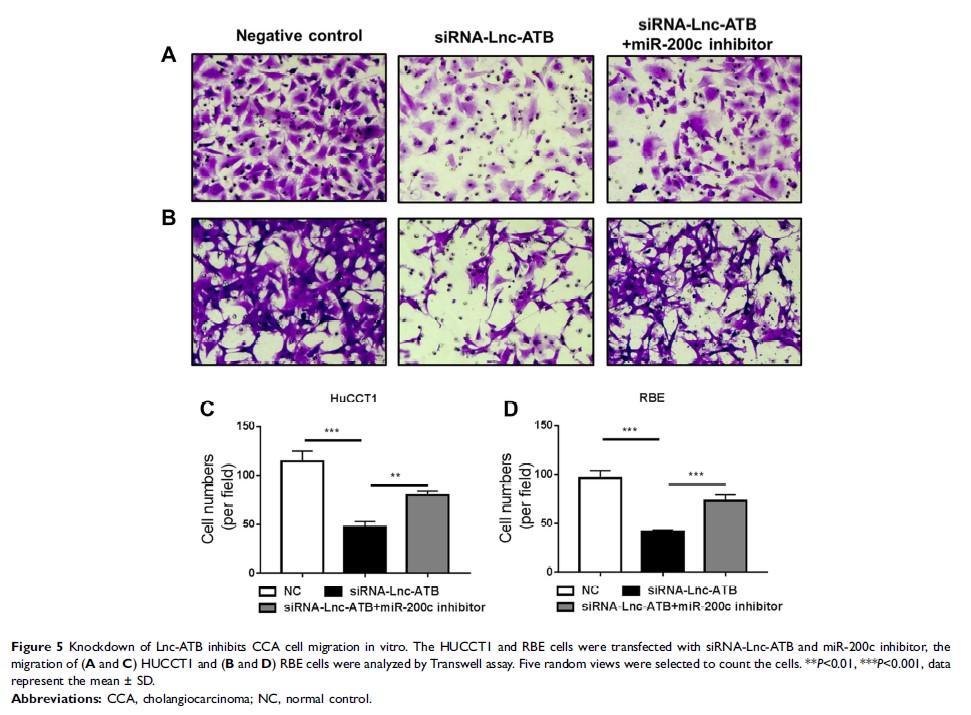
Results: CCA tissues have increased Lnc-ATB and reduced miR-200a/b/c levels, but the down-regulated miR-200c was most prominent. Up-regulated Lnc-ATB significant negatively correlated with miR-200c and predicted advanced TNM stage and more lymph node metastasis of CCA patients. Knockdown of Lnc-ATB in two CCA cell lines HuCCT1 and RBE increased miR-200c levels. The luciferase reporter assay further confirmed the direct binding site of miR-200c in Lnc-ATB. Inhibition of Lnc-ATB significantly impaired cell vitality and induced apoptosis and G0/G1 arrest, which, however, was rescued by miR-200c inhibitor. The ability of migration of CCA cells was also up-regulated by Lnc-ATB but was suppressed by miR-200c. Mechanistically, the cell cycle-related CCND1/CDK2, apoptosis-related BCL-2/caspase-3 and EMT-related E-cadherin/ZEB1/2 were regulated by Lnc-ATB via miR-200c. Knockdown of Lnc-ATB in vivo up-regulated miR-200c signals to inhibit tumor growth with decreased PCNA expression in tumor tissues, which was restored by miR-200c inhibition.
Conclusion: Overexpressed Lnc-ATB functioned as an oncogene for CCA growth and metastasis via miR-200 signals.
Keywords: Lnc-ATB, miR-200, growth, EMT, cholangiocarcinoma