108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

沉默 circZFR 通过调节 miR-206 抑制人肾癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Wang M, Gao Y, Liu J
Received 8 May 2019
Accepted for publication 27 August 2019
Published 13 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7537—7550
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215012
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most prevalent kind of kidney cancer. At present, the most efficient treatment mean is surgery. 40% patients with clear cell RCC (ccRCC) relapse after surgery. Identifying novel therapeutic markers and spots for early detection and treatment of RCC is necessary.
Methods: qRT-PCR was utilized to quantify circZFR and miR-206 expression in CAKI-1 and ACHN cells. Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay. Colony formation capacity was measured by colony formation assay. Transwell assay was utilized to investigate migration and invasion capacity. Expression of migration and apoptosis-associated proteins was quantified by Western blot.
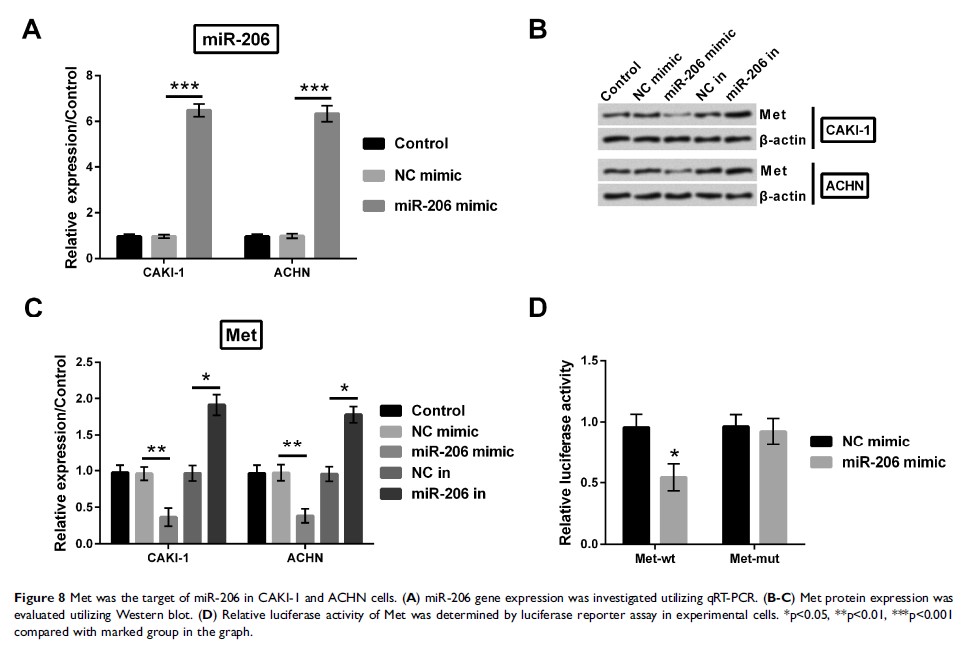
Results: As a result, circZFR was highly expressed in RCC tissues and cells. Si-circZFR suppressed cell growth, migration and invasion of experimental cells. In addition, knockdown of circZFR upregulated miR-206 expression. Moreover, the antigrowth, antimigrating and anti-invasive effects of si-circZFR were attenuated when downregulating miR-206. Furthermore, Met is the target gene of miR-206 in experimental cells. The suppression on these signaling pathways was acted by targeting miR-206/Met axis.
Conclusion: The results demonstrated si-circZFR inhibited cell growth, migration and invasion in experimental cells by up-regulating of miR-206. Furthermore, si-circZFR suppressed Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathways via targeting miR-206/Met axis.
Keywords: circZFR, miR-206, renal carcinoma cells