108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

UBE2T 通过 G2/M 检查点促进肝细胞癌的增殖
Authors Liu LL, Zhu JM, Yu XN, Zhu HR, Shi X, Bilegsaikhan E, Guo HY, Wu J, Shen XZ
Received 23 January 2019
Accepted for publication 19 August 2019
Published 13 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8359—8370
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S202631
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Growing evidence suggests that the ubiquitin-proteasome system is involved in the pathogenesis and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); yet, little is known about the role of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (UBE2T) in HCC.
Materials and methods: UBE2T levels were detected in HCC tissues and hepatoma cell lines using quantitative reserve transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis. Next, the changes of phenotypes after UBE2T knockdown or overexpression were evaluated using in vitro methods. Finally, the mechanism of UBE2T in HCC was tested using ex vivo and in vivo methods.
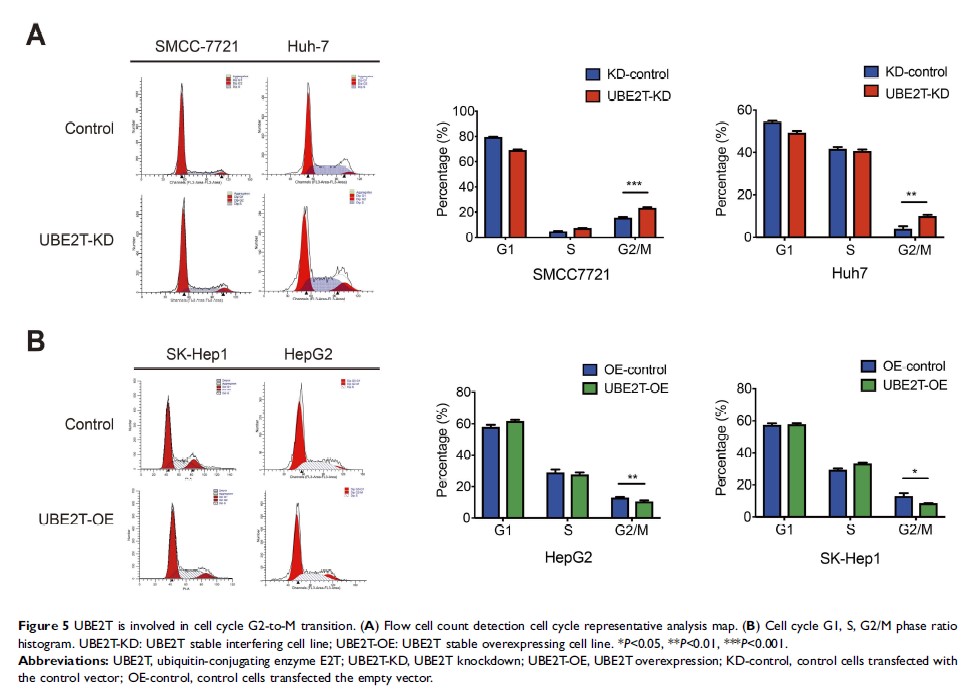
Results: In the present study, we reported that UBE2T mRNA and protein levels were significantly upregulated in HCC tissues compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues. Additionally, suppression of UBE2T expression inhibited proliferation, colony formation, tumorigenesis, migration, and invasion of hepatoma cells, whereas UBE2T overexpression led to the opposite outcomes. Moreover, suppression of UBE2T expression resulted in an increase in G2/M phase and a decrease in the percentage of cells in G1 phase, which indicated a cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. In contrast, the percentage of cells in G2/M phase decreased following UBE2T overexpression. Further study indicated that UBE2T regulated the G2/M transition by modulating cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1.
Conclusion: Taken together, the findings of the present study uncover biological functions of UBE2T in hepatoma cells, and delineate preliminary molecular mechanisms of UBE2T in modulating HCC development and progression.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, UBE2T, ubiquitination, cell cycle