108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载 3,5,4'-三甲氧基-反式-二苯乙烯的 PEG-PE 胶束用于治疗结肠癌
Authors Wu JY, Li YJ, Liu XY, Cai JX, Hu XB, Wang JM, Tang TT, Xiang DX
Received 2 July 2019
Accepted for publication 30 August 2019
Published 12 September 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 7489—7502
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S221625
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: 3,5,4′-trimethoxy-trans-stilbene (BTM) is a methylated derivative of resveratrol. To improve the pharmaceutical properties of BTM, BTM loaded PEG-PE micelles (BTM@PEG-PE) were fabricated and its anti-cancer efficacy against colon cancer was evaluated.
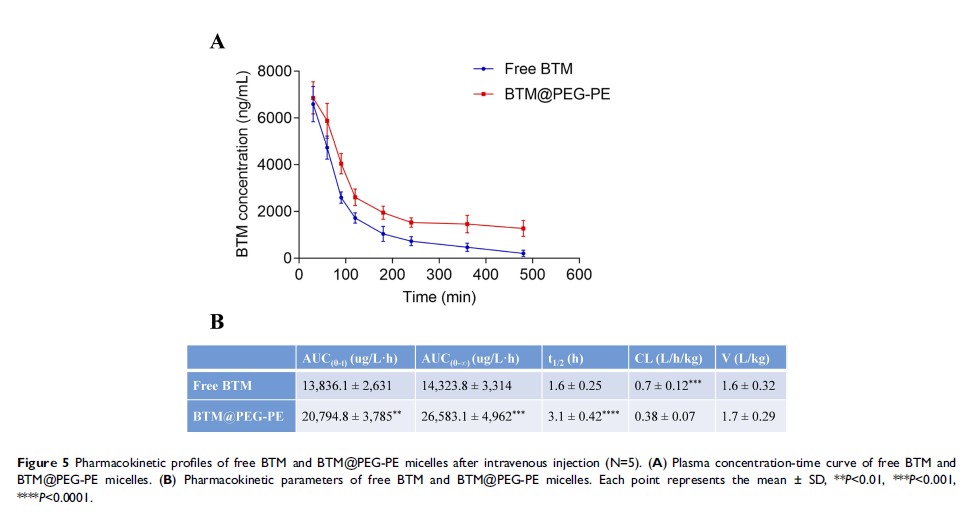
Methods: BTM@PEG-PE micelles were prepared by the solvent evaporation method and were characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), size, zeta potential, polymer disperse index (PDI) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Cellular uptake, cell viability assay, caspase-3 activity assay and flow cytometry were performed to evaluate the cell internalization and anti-cancer efficacy of BTM@PEG-PE micelles in vitro. Pharmacokinetic profiles of BTM and BTM@PEG-PE micelles were compared and in vivo anti-cancer therapeutic efficacy and safety of BTM@PEG-PE micelles on CT26 xenograft mice were evaluated.
Results: BTM was successfully embedded in the core of PEG-PE micelles, with a drug loading capacity of 5.62±0.80%. PEG-PE micelles facilitated BTM entering to the CT26 cells and BTM@PEG-PE micelles exerted enhanced anti-cancer efficacy against CT26 cells. BTM@PEG-PE micelles showed prolonged half-life and increased bioavailability. More importantly, BTM@PEG-PE micelles treatment suppressed tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice and prolonged survival with minimal damage to normal tissues.
Conclusion: Altogether, the BTM@PEG-PE micelles might be a promising strategy to enhance the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic potentials of BTM for colon cancer therapy.
Keywords: 3,5,4′-trimethoxy-trans-stilbene, bioavailability, colon cancer, drug delivery, micelles