108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白细胞介素 11 的遗传变异体和幽门螺杆菌感染之间的相互作用对胃癌易感性的影响
Authors Liao C, Hu S, Zheng Z, Tong H
Received 2 May 2019
Accepted for publication 24 July 2019
Published 11 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7459—7466
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S214238
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) ranks the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. We aimed to clarify the relevance of genetic variants of IL-11 , a hub of various carcinogenic pathways, as well as their interactions with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori ) infection in the development of GC.
Methods: A case–control study with 880 GC cases and 900 healthy controls was conducted in a Chinese population. Six tagSNPs were detected by Taqman Allelic Discrimination assay, while H. pylori status was detected by Typing Detection Kit for Antibody to H. pylori and serum IL-11 level was measured using ELISA method.
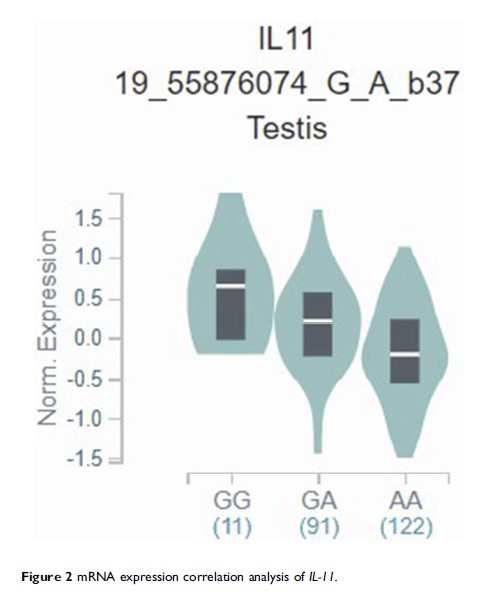
Results: We found that rs1126760 (C vs T: OR=1.39, 95% CIs=1.13–1.70, P =0.002) and rs1126757 (C vs T: OR=0.82, 95% CIs=0.72–0.93, P =0.002) were significantly associated with susceptibility of GC. Even adjusted for Bonferroni correction, the results were still significant (P =0.002×6=0.012). IL-11 rs1126760 was significantly associated with higher serum and expression level of IL-11 , while rs1126757 was significantly associated with lower serum IL-11 level (P <0.001). Significant interaction with H. pylori infection was identified for rs1126760 (P for interaction =0.005). Higher expression of the IL-11 gene was significant with development and poor prognosis of GC.
Conclusion: Our study provides strong evidence that genetic variants of the IL-11 gene may interact with H. pylori infection and contribute to the development of GC. Further studies with larger sample size and functional experiments are needed to validate our findings.
Keywords: gastric cancer, polymorphism, IL-11 , Helicobacter pylori