108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

上调的长非编码 RNA DUXAP8 通过抑制人类肝细胞癌中 Krüppel 样因子 2 表达来促进细胞生长
Authors Jiang H, Shi X, Ye G, Xu Y, Xu J, Lu J, Lu W
Received 3 May 2019
Accepted for publication 19 July 2019
Published 11 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7429—7436
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S214336
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background and aim: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are implicated as novel factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Although thousands of lncRNAs have been discovered, only a small portion have been functionally determined in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we aimed to comprehensively analyze differentially expressed lncRNAs, evaluate their clinical significance, and explore the functional roles and underlying mechanism in HCC.
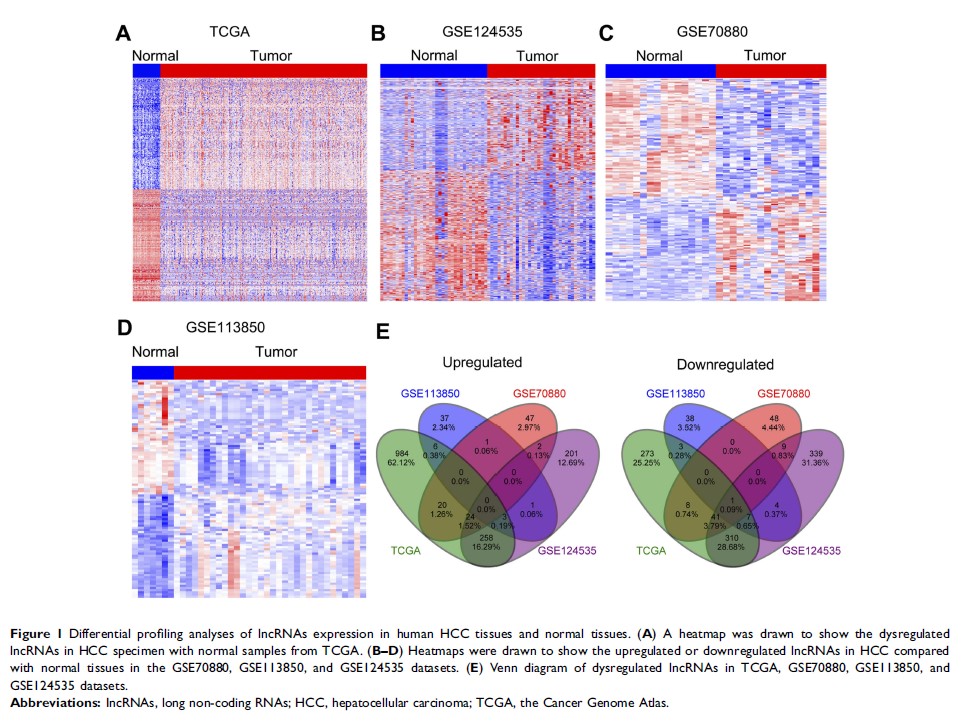
Methods: We identified hundreds of lncRNAs which were dysregulated in HCC tissues through performing integrative analyses using the RNA sequencing data and independent gene microarray data from Gene Expression Omnibus and the Cancer Genome Atlas.
Results: Dysregulated DUXAP8, LINC01116, LINC01138, and PCAT6 are significantly associated with HCC patients’ poor outcomes. Further experimental validation revealed that down-regulation of lncRNA DUXAP8 inhibited HCC cells proliferation and colony formation ability. Mechanistically, DUXAP8 repressed tumor suppressor KLF2 transcription through interacting with histone-lysine N-methyltransferase enzyme enhancer of zeste homolog 2.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings can provide a valuable resource of HCC-associated lncRNAs and new insights into the biological functions of lncRNAs in HCC development.
Keywords: HCC, lncRNAs, DUXAP8, EZH2, KLF2