108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

12-脂氧合酶通过 TGF-β1 介导的上皮向间质转化促进肿瘤进展,并预测食管鳞状细胞癌的预后不良
Authors Qu Y, Wen Z, Mi S, Chen P, Wang J, Jia Y, Cheng Y
Received 16 April 2019
Accepted for publication 25 August 2019
Published 11 September 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 8303—8313
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S212478
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Purpose: To clarify the effect of 12-lipoxygenase/12-hydroxyeicosatetraeonic acid (12-LOX/12-HETE) on progress of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and the possible mechanism.
Patients and methods: We performed cell experiments including chemical treatment, transfection, Western blotting and transwell assay to investigate the function of 12-LOX/12-HETE. Slices of tumor tissues were obtained from ESCC patients treated in Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining was done to find their correlation with prognosis and clinicopathological characteristics.
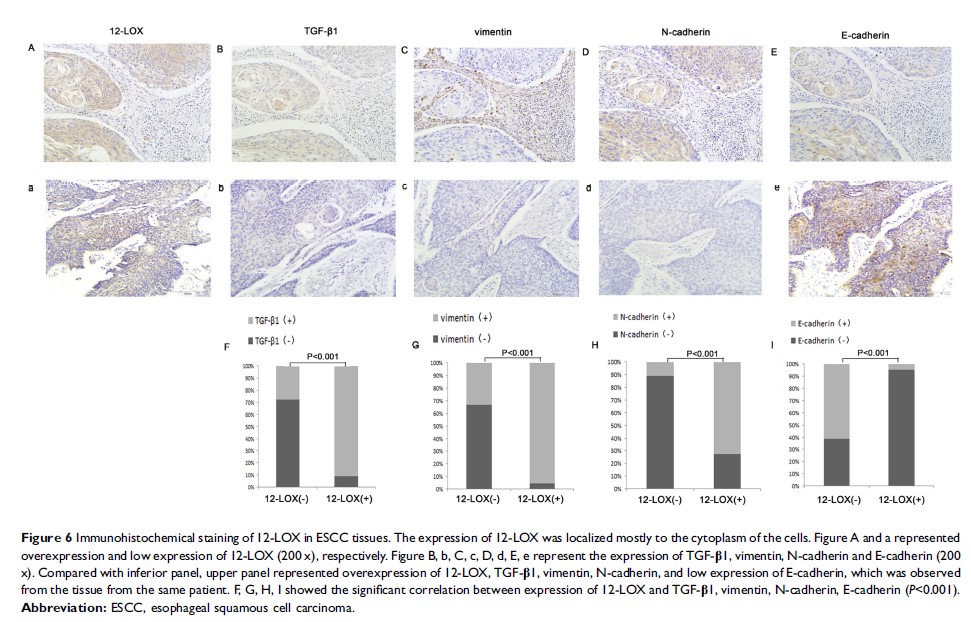
Results: In ESCC cells, inhibition of 12-LOX caused a decrease in transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) level, and abilities of migration and invasion were also inhibited. Nevertheless, the inhibition could be partly relieved when treated with 12-HETE or TGF-β1. Analyses of IHC staining indicated a positive correlation between the expression of 12-LOX and EMT level, and an inverse correlation between 12-LOX and overall survival (OS). Univariate and multivariate analyses further suggested that 12-LOX was an independent prognostic factor for ESCC patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study proved that 12-LOX/12-HETE-promoted tumor migration and invasion might partly be through TGF-β1-mediated EMT in ESCC, and 12-LOX could be a promising biomarker for predicting prognosis in ESCC patients.
Keywords: 12-LOX, 12-HETE, Baicalein, tumor metastasis, overall survival