108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

起始转移性鼻咽癌姑息化疗,伴或不伴抗 EGFR 治疗:倾向评分匹配研究
Authors Sun XS, Liang YJ, Li XY, Liu SL, Chen QY, Tang LQ, Mai HQ
Received 10 May 2019
Accepted for publication 1 September 2019
Published 10 September 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3207—3216
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S215190
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tin Wui Wong
Objective: We aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of cetuximab (CTX) or nimotuzumab (NTZ) on the addition of palliative chemotherapy (PCT) in patients with de novo metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
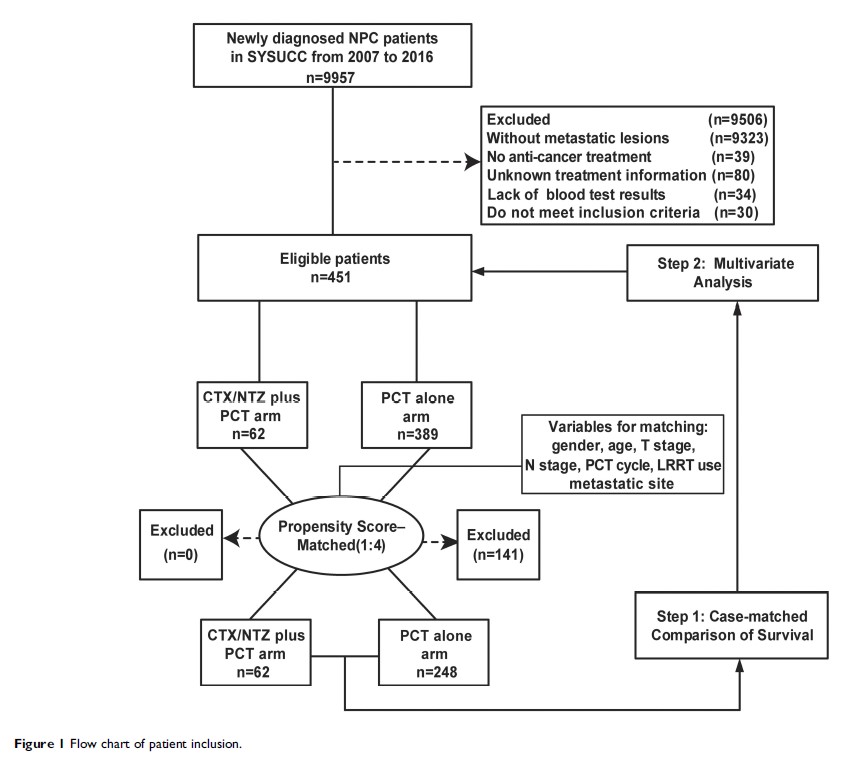
Materials and methods: From 2007 to 2016, 451 eligible patients with de novo metastatic NPC were enrolled in the study. With propensity score matching technique, we created a well-balanced cohort by matching patients who received CTX/NTZ plus PCT (62 patients) with those receiving PCT alone (248 patients) in a ratio of 1:4. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). All potential prognostic factors were involved in the multivariate analysis with the Cox regression hazards model. Kaplan–Meier curves were used to compare the survival status, and log-rank test to measure the significance.
Results: The median follow-up time was 27.7 months (range, 1–126 months). No significant difference in survival was observed between the CTX/NTZ plus PCT group and PCT group. (3-year OS: 63.0% vs 58.1%; P =0.485). The administration of CTX/NTZ was not found to be an independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis. With regard to toxicity, the development of a G3-4 skin reaction and mucositis was more common in patients receiving CTX plus PCT. Interaction effects analysis did not show any significant interaction effects on OS between the treatment regimen and prognostic factors (P >0.05).
Conclusion: The efficacy of CTX/NTZ and PCT is comparable to single PCT treatment in terms of survival outcomes among de novo metastatic NPC patients. Moreover, the application of CTX exacerbated skin reactions and mucositis.
Keywords: targeted drug, chemotherapy, treatment, nasopharyngeal carcinoma and overall survival