108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CYP3A4 等位基因变异对洛哌丁胺体外代谢的功能特征
Authors Lin QM, Li YH, Liu Q, Pang NH, Xu RA, Cai JP, Hu GX
Received 9 May 2019
Accepted for publication 8 August 2019
Published 10 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2809—2817
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S215129
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background: Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) appears to be genetically polymorphic, which in turn contributes to interindividual variability in response to therapeutic drugs. Loperamide, identified as a CYP3A4 substrate, is prone to misuse and abuse and has high risks of life-threatening cardiotoxicity.
Methods: Thus, this study is designed to evaluate the enzymatic characteristics of 29 CYP3A4 alleles toward loperamide in vitro, including the 7 novel CYP3A4 variants (*28–*34). The incubation system (containing CYP3A4 enzyme, cytochrome b5, 0.5–20 μM loperamide, potassium phosphate buffer and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) was subject to 40-mins incubation at 37°C and the concentrations of N-demethylated loperamide were quantified by UPLC-MS/MS.
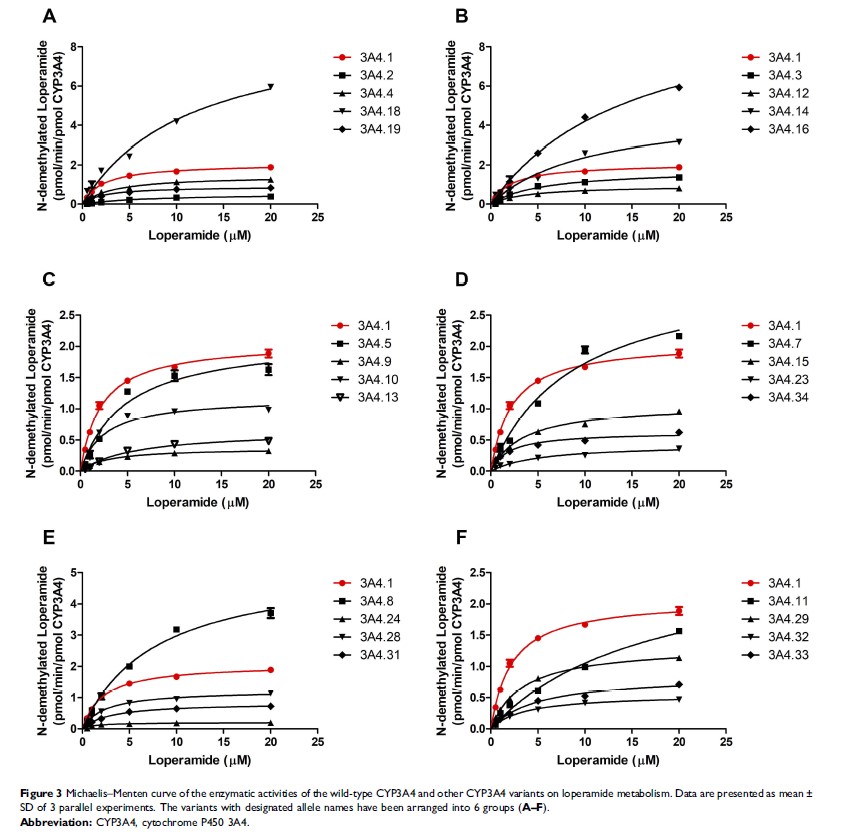
Results: As a result, CYP3A4.6, .17, .20 and .30 showed extremely low activity or no activity and the rest of CYP3A4 variants presented varying degrees of decrements in catalytical activities when compared with CYP3A4.1.
Conclusion: As the first study to identify the properties of these CYP3A4 variants toward loperamide metabolism, our investigation may establish the genotype–phenotype relationship for loperamide, predict an individual’s capability in response to loperamide, and provide some guidance of clinical medication and treatment for loperamide.
Keywords: CYP3A4, genetic polymorphism, interindividual variability, loperamide, misuse and abuse, cardiotoxicity, personalized treatment