108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

阿法替尼对具有罕见 EGFR delE709_T710insD 突变的肺腺癌患者的巨大疗效:一例病例报告
Authors An N, Wang H, Zhu H, Yan W, Jing W, Kong L, Zhang Y, Yu J
Received 2 July 2019
Accepted for publication 25 August 2019
Published 10 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7399—7404
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S221638
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
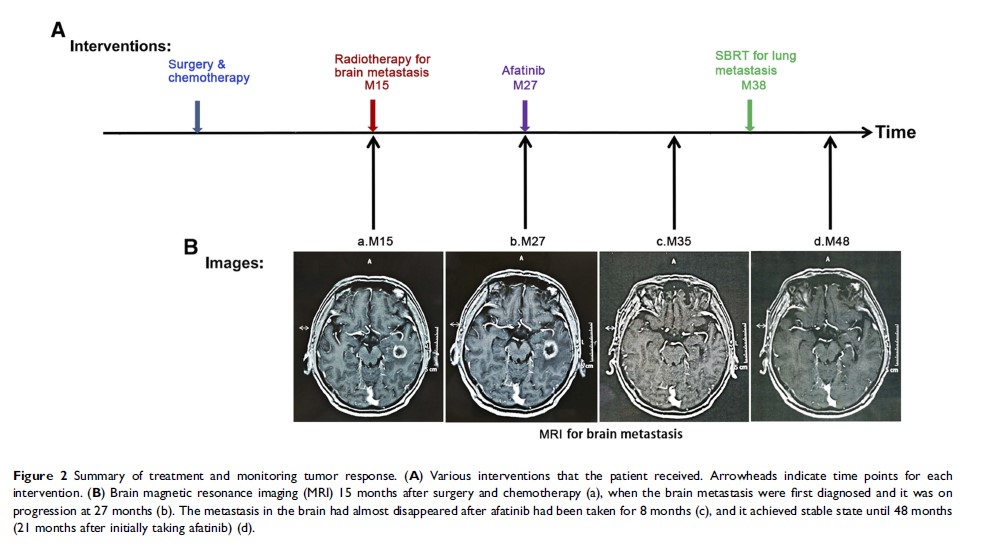
Abstract: EGFR)-targeted drugs have been the first-line treatment for patients with EGFR -mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), especially exon 19 deletions and L858R mutation in exon 21. However, there is insufficient evidence for other less common types of EGFR mutations, such as delE709_T710insD (del 18). Recent studies have revealed that these rare genotypes could be targetable if appropriate mutations, such as delE709_T710insD (del 18). Recent studies have revealed that these rare genotypes could be targetable if appropriate EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors are selected. Here we reported a stage Ⅳ NSCLC patient with delE709_T710insD mutation who responded well to afatinib, a second-generation TKI. Afatinib had taken good control of the patient’s brain metastasis with a progression-free survival of 11 months and an overall survival exceeded 21 months, although he had received multi-line therapy. This case demonstrates EGFR delE709_T710insD is a rare but potentially afatinib responsive mutation in NSCLC, which may contribute to changes in clinical practice and further research into the precise detection and treatment of rare mutations in EGFR .
Keywords: non-small-cell lung cancer, epidermal growth factor receptor, molecular targeted therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, afatinib, EGFR rare mutation