108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过在肝癌中抑制 CD14 可遏制 stomatin 样蛋白 2,从而减弱肿瘤进程和炎症反应
Authors Pu X, Dong C, Zhu W, Li W, Jiang H
Received 9 May 2019
Accepted for publication 2 August 2019
Published 9 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7361—7373
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215131
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is involved in the inflammation in liver cancer. High-expressed stomatin-like protein 2 (SLP-2) is commonly reported in many cancer types. This study aims to investigate the functions of SLP-2 in TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses and tumor progression of liver cancer.
Patients and methods: Plasmid transfection technique was applied to silence and overexpress genes. Changes in cell viability and apoptosis were determined by performing cell counting kit-8 assay and flow cytometry. The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by ELISA. We further measured the several types of the malignant transformation of SK-Hep1 cells to assess the effects of SLP-2 silencing on the cell migration and invasion, proliferation and angiogenesis of liver cancer in vitro. Western blot and RT-qPCR were performed for expression analysis.
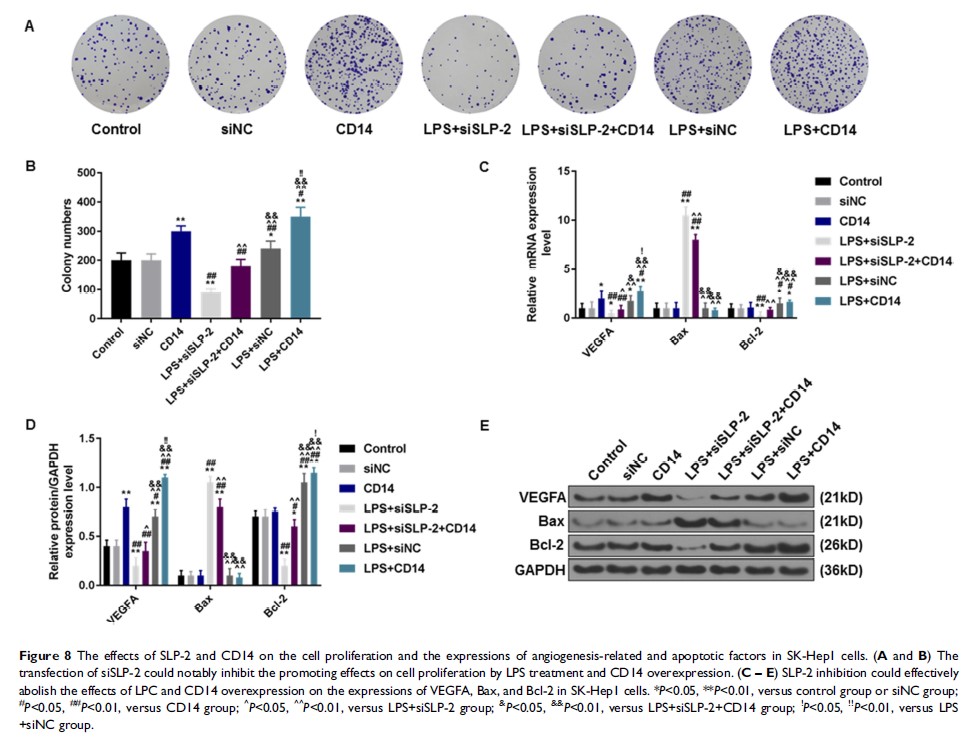
Results: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promoted the cell proliferation of SK-Hep1 and production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and IL-6. SLP-2 silencing could inhibit the protein and mRNA levels of CD14 and Cdc42 and subsequently inhibited the levels of TNF-α and IL-6. Overexpressed CD14 not only remarkably reversed the proapoptotic ability of SLP-2 silencing and promoted the expression of Cdc42 and production of TNF-α and IL-6, but also notably reversed the inhibitory effects on the malignant abilities of SK-Hep1 cells by SLP-2 silencing.
Conclusion: SLP-2 silencing could significantly attenuate the inflammatory responses and tumor progression of liver cancer via inhibiting LPS/TLR4 signal transduction through the repression of CD14.
Keywords: liver cancer, stomatin-like protein 2, Toll-like receptor 4, apoptosis, inflammatory response