108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

KRAS rs7973450 A>G 增加中国儿童神经母细胞瘤的风险:一项四中心病例对照研究
Authors Lin A, Hua RX, Tang J, Zhu J, Zhang R, Zhou H, Zhang J, Cheng J, Xia H, He J
Received 15 July 2019
Accepted for publication 30 August 2019
Published 5 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7289—7295
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S223220
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Neuroblastoma is one of the most common extracranial solid pediatric tumors. KRAS plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in KRAS have been shown to modify susceptibility to multiple tumors, but no specific molecular epidemiology study was reported regarding neuroblastoma.
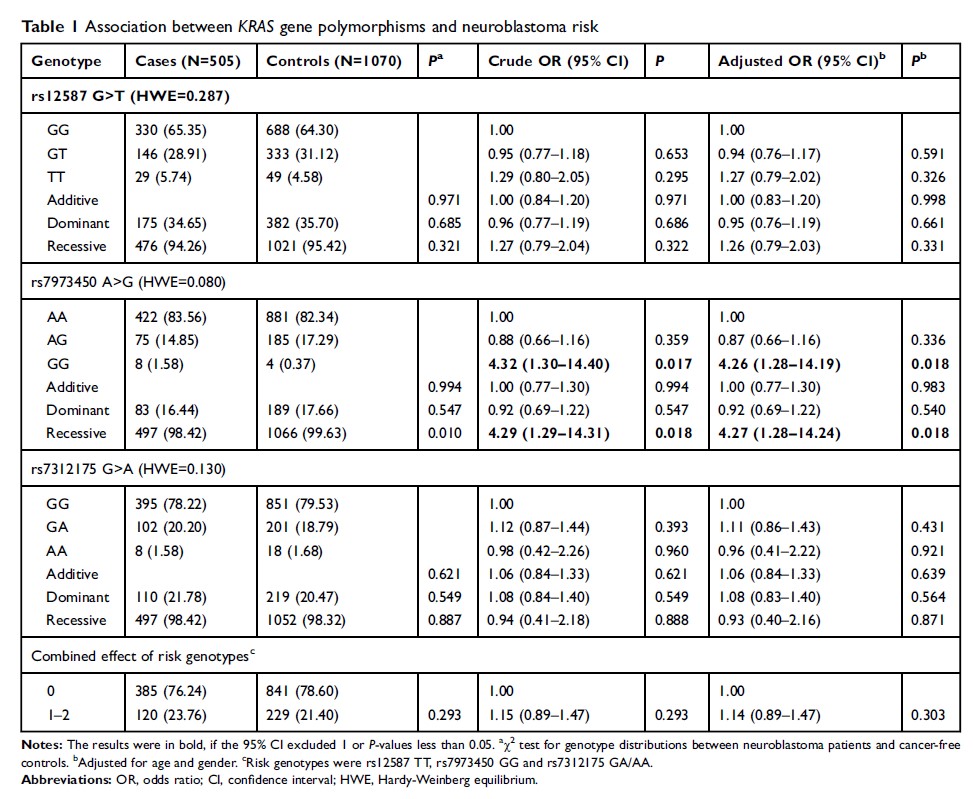
Methods: We conducted a four-center case-control study to explore the association between KRAS gene polymorphisms (rs12587 G>T, rs7973450 A>G, rs7312175 G>A) and neuroblastoma susceptibility with 505 Chinese children and 1070 matched controls.
Results: We found that rs7973450 A>G was associated with significantly increased neuroblastoma risk [GG vs. AA: adjusted odds ratio (OR)=4.26, 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.28–14.19, P =0.018; GG vs. AA/AG: adjusted OR=4.27, 95% CI=1.28–14.24, P =0.018]. The stratified analysis further demonstrated that rs7973450 GG genotype carriers had a higher risk to develop neuroblastoma in the subgroups of males, tumor originated from the adrenal gland and clinical stages III+IV.
Conclusions: Overall, our results suggested that rs7973450 A>G was associated with increased neuroblastoma risk.
Keywords: neuroblastoma, KRAS , polymorphism, susceptibility