108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

右美托咪定或舒芬太尼分别与罗哌卡因结合用于开胸术后硬膜外镇痛的比较:一项随机对照研究
Authors Yan MJ, Wang T, Wu XM, Zhang W
Received 8 March 2019
Accepted for publication 2 August 2019
Published 5 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2673—2678
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S208014
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Ueberall
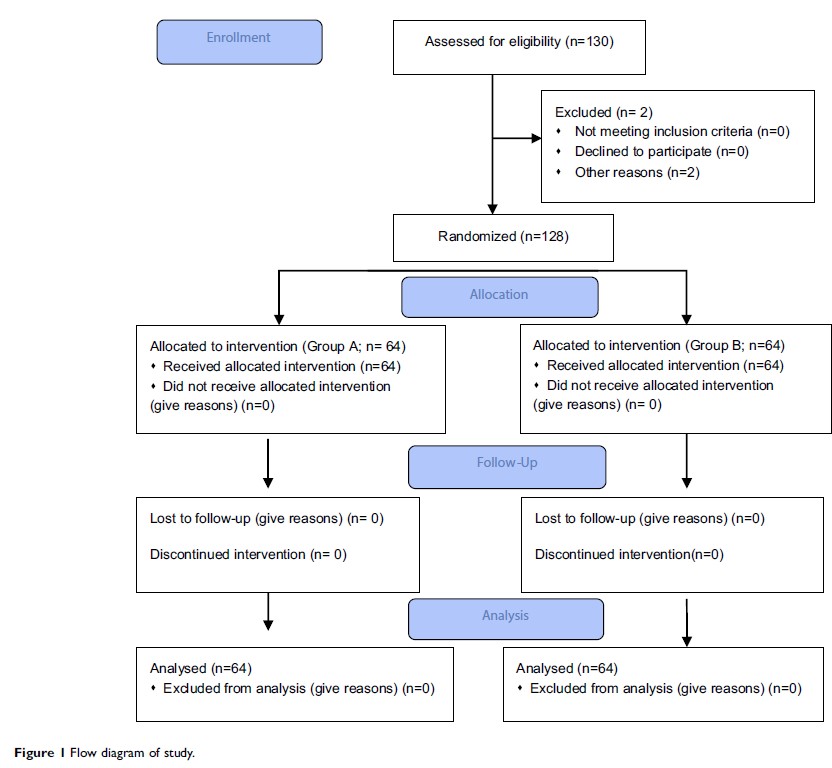
Background: Thoracotomy is frequently accompanied with moderate-to-severe postoperative pain, and excellent pain management is important for early rehabilitation. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine for epidural analgesia after thoracotomy.
Methods: One hundred and thirty patients undergoing elective lung lobectomy were enrolled in the double-blind study and randomly divided into two groups. Group A received 0.5 μg/mL of dexmedetomidine plus 0.1% ropivacaine for postoperative analgesia, and group B (control group) received 0.5 μg/mL of sufentanil plus 0.1% ropivacaine for postoperative analgesia. Hemodynamic parameters were monitored. Pain intensity at rest was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS) at 2, 4, 6,8, 12, 24, and 48 hrs postoperatively. Ramsay sedation score (RSS), analgesic consumption, postoperative respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting, pruritus, and bradycardia were recorded.
Results: The VAS values at rest during the postoperative 6–48 hrs were lower in group A than those in group B (P <0.05), and the RSS values were higher in group A during the postoperative 4–48 hrs compared to group B (P <0.05). Side effects were similar between the groups (P >0.05).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine may provide better postoperative analgesia and sedative effect in patients undergoing thoracic surgery with fewer side effects. It is superior to sufentanil in analgesic effect during postoperative analgesia after thoracotomy.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine, sufentanil, ropivacaine, epidural, analgesia