108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

BLT1 拮抗剂对 COPD 的治疗潜力:参与诱导自噬和改善炎症
Authors Zhang L, Huang J, Dong R, Feng Y, Zhou M
Received 12 May 2019
Accepted for publication 10 August 2019
Published 4 September 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3105—3116
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S215433
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios D. Panos
Purpose: Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a major pro-inflammatory mediator that leads to the persistence of chronic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The purpose of this study was to evaluate therapeutic potential of BLT1 antagonist for cigarette smoke (CS)-induced COPD and to explore the underlying mechanism.
Materials and methods: In vitro, autophagy proteins were determined by Western blotting in RAW264.7 macrophages treated with U75302 (BLT1 antagonist) or autophagy inhibitor in cigarette smoke extract-induced inflammation. In vivo, C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into three groups: Control group, CS group and CS+U75302 group. After 12-week exposure, histological analysis and lung function tests were performed to evaluate the inflammatory infiltration and emphysema. The expression of inflammatory cytokines was measured by real-time PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Immunohistochemical analysis and Western blotting detected the expression of autophagy-related proteins. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed the alterations of autophagosomes and lysosomes.
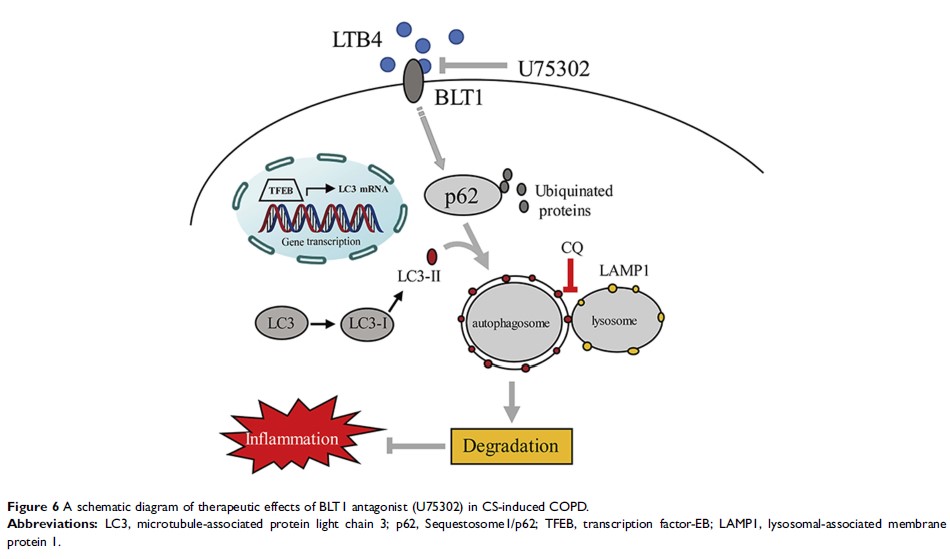
Results: Lower levels of inflammatory factors and autophagy markers were detected in U75302-treated cells and mice after CS exposure than control. In vitro, LC3 mRNA expression was elevated when treated with U75302. Autophagy inhibition resulted in augmented inflammatory response and autophagy proteins even with U75302 treatment. Furthermore, BLT1 antagonist decreased the number of lysosomes and autophagosomes in alveolar macrophages of mice and potentially enhanced the expression of transcriptional activation of transcription factor-EB (TFEB) in vitro and vivo.
Conclusion: Insufficient autophagy of macrophages was associated with LTB4-mediated inflammation in CS-exposure models. BLT1 antagonist ameliorated inflammatory response through inducing autophagy.
Keywords: cigarette smoke, inflammation, autophagy, BLT1 antagonist, COPD