108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在 ICU 接受治疗的患者的凝血生物标志物可预测由腹腔内感染引起的败血性休克患者的急性肾损伤和死亡率
Authors Xu Z, Cheng B, Fu S, Liu X, Xie G, Li Z, Ji Y, Fu Q, Xu Z, Fang X
Received 6 June 2019
Accepted for publication 26 August 2019
Published 4 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2755—2764
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S218592
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Purpose: Sepsis-associated coagulopathy (SAC) contributes to the development of multiple organ failure (MOF) and increasing mortality. The present study was conducted to investigate whether coagulative biomarkers on admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) can predict acute kidney injury (AKI) and mortality in patients with septic shock caused by intra-abdominal infection (IAI).
Patients and methods: An observational retrospective study was conducted in the surgical ICU. We studied patients who met the criteria of septic shock (Sepsis-3) caused by IAI between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2016. By adjusting for baseline characteristics, multivariate regression analyses were employed to identify independent risk factors for predicting AKI and mortality.
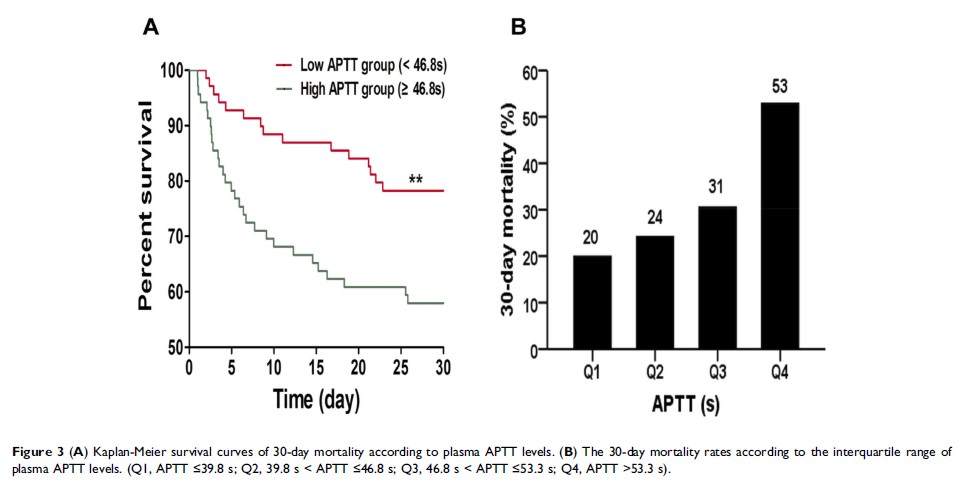
Results: Of the 138 enrolled patients, 65 patients developed AKI. The patients who developed AKI exhibited a dramatically higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (median, 12), Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score (median, 27.5) and mortality rate. In both models, we found that activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) (odds ratio (OR)=1.074, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.030–1.120, p =0.001), prothrombin time (PT) (OR=1.162, 95% CI 1.037–1.302, p =0.010) and D-dimer level (OR=1.098, 95% CI 1.002–1.202, p =0.045) on admission to the ICU were significant risk factors for AKI. Moreover, Cox regression analysis showed that prolonged APTT (OR=1.065, 95% CI 1.025–1.107, p =0.001) was independently associated with high mortality.
Conclusion: In patients with septic shock caused by IAI, APTT, PT and D-dimer level on admission to the ICU were significantly associated with AKI. Furthermore, APTT was an independent predictor of 30-day mortality.
Keywords: coagulopathy, biomarker, septic shock, acute kidney injury, intra-abdominal infection, mortality