108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

聚多巴胺修饰的双配体纳米颗粒作为高效的磁共振/光声双峰血栓靶向造影剂
Authors Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Ye M, Xu J, Liu J, Zhou J, Wang S, Guo D, Wang Z, Ran H
Received 21 May 2019
Accepted for publication 1 August 2019
Published 3 September 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 7155—7171
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S216603
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
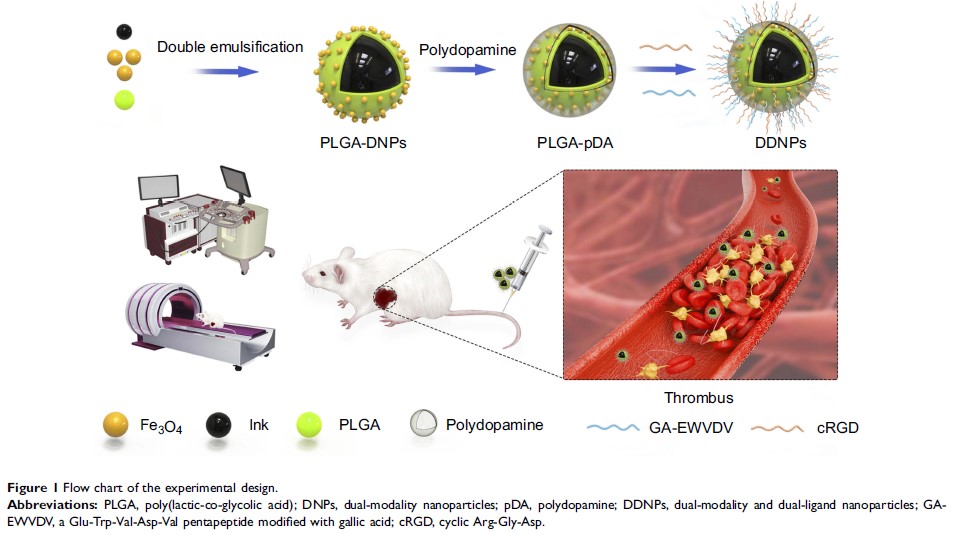
Background: Platelet activation and subsequent aggregation are the initial stages of thrombosis. A molecular probe that specifically targets activated platelets and remains retained under high shear stress in vivo can enhance the imaging effect to achieve early and accurate diagnosis.
Methods and materials: In this study, we constructed nanoparticles (NPs) using polydopamine to carry two peptides that simultaneously bind integrin αIIbβ3 and P-selectin on activated platelets to enhance the targeting of NPs to thrombus.
Results: The targeting specificity and binding stability of the NPs on red and white thrombi were demonstrated in vitro using a simulated circulatory device and the targeting effect of the NPs on mixed thrombus was studied by magnetic resonance (MR)/photoacoustic (PA) dual-modality imaging in vivo. NPs that were surface modified with both peptides have higher selectivity and retention to red and white thrombi in vitro than NPs with a single or no peptide, and the targeting effect was closely related to the number and distribution of activated platelets as well as the structure and type of thrombus. The NPs also have MR/PA dual-modality imaging functionality, significantly enhancing the imaging of mixed thrombus in vivo.
Conclusion: These dual-targeted NPs have improved targeting specificity and binding stability to different thrombi under high shear stress and are beneficial for the early diagnosis of thrombosis.
Keywords: dual-modality, dual-ligand, targeting effect, thrombus, magnetic resonance imaging, photoacoustic imaging