108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA XIST 耗竭可通过上调 microRNA-424-5p 抑制 bFGF 来阻止侵袭性垂体神经内分泌肿瘤的癌症进展
Authors Zhou K, Li S, Du G, Fan Y, Wu P, Sun H, Zhang T
Received 11 March 2019
Accepted for publication 30 July 2019
Published 2 September 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 7095—7109
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S208329
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are vital mediators in human cancers including pituitary neuroendocrine tumor (PitNET) and could function as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) of microRNAs (miRNAs). The main objective of this study is to identify effect of lncRNA X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) and microRNA-424-5p (miR-424-5p) on PitNET.
Methods: Microarray analysis was employed to identify the PitNET-related differentially expressed lncRNAs. PitNET tissues, including both invasive and non-invasive subtypes in parallel with normal pituitary tissues were collected for the determination of the expression of XIST, miR-424-5p and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and the interaction among them. Subsequently, the expression of XIST, miR-424-5p and bFGF in PitNET cells was altered to elucidate their biological significance in the aspects of proliferation, migration, invasion, and the apoptosis.
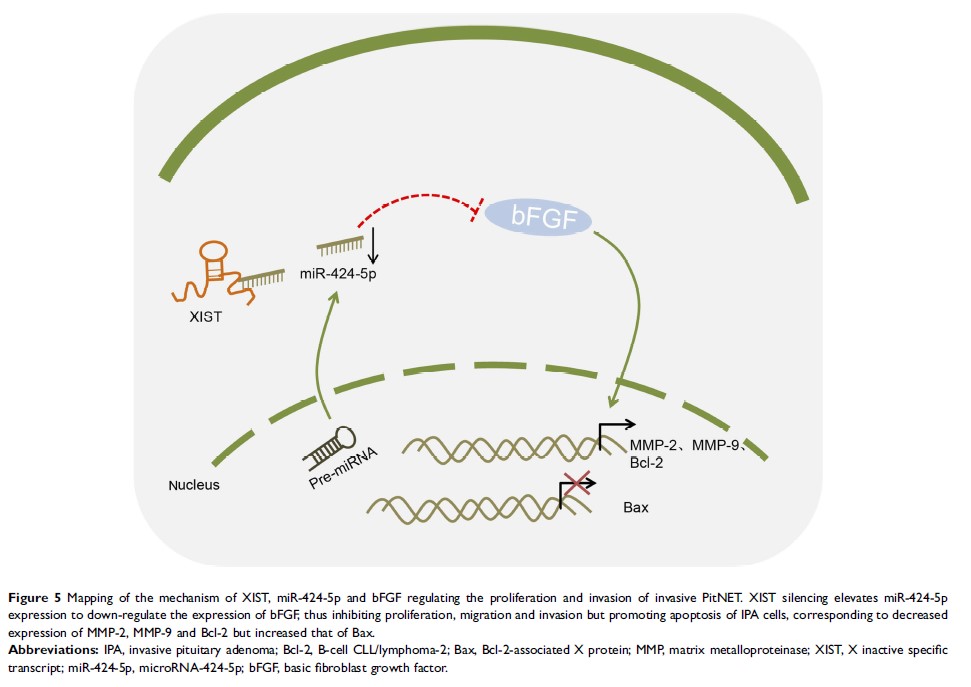
Results: Both XIST and bFGF exhibited high expression, but miR-424-5p had a low expression in invasive PitNET tissues as compared to non-invasive PitNET normal pituitary tissues. Additionally, XIST competitively bound to miR-424-5p to elevate the expression of bFGF. Furthermore, depleted XIST or bFGF, or elevated miR-424-5p was revealed to suppress the proliferation, migration, invasion, and promote cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of invasive PitNET cells. miR-424-5p repressed the proliferation, migration, invasion of invasive PitNET cells by targeting bFGF.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the fundamental findings of the present study suggested that the functional suppression of XIST downregulated bFGF to inhibit the development of PitNET by increasing miR-424-5p expression, proposing XIST as a novel therapeutic target for PitNET.
Keywords: invasive pituitary neuroendocrine tumor, lncRNA XIST, microRNA-424-5p, bFGF, invasion, migration