109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

受低频率振幅波动打扰的原发性闭角型青光眼患者的自发大脑活动模式:一个功能性磁共振成像 (fMRI) 研究
Authors Huang X, Zhong YL, Zeng XJ, Zhou F, Liu XH, Hu PH, Pei CG, Shao Y, Dai XJ
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1877—1883
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S87596
Received 29 April 2015, Accepted 8 June 2015, Published 29 July 2015
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Approved for publication by Professor Wai Kwong Tang
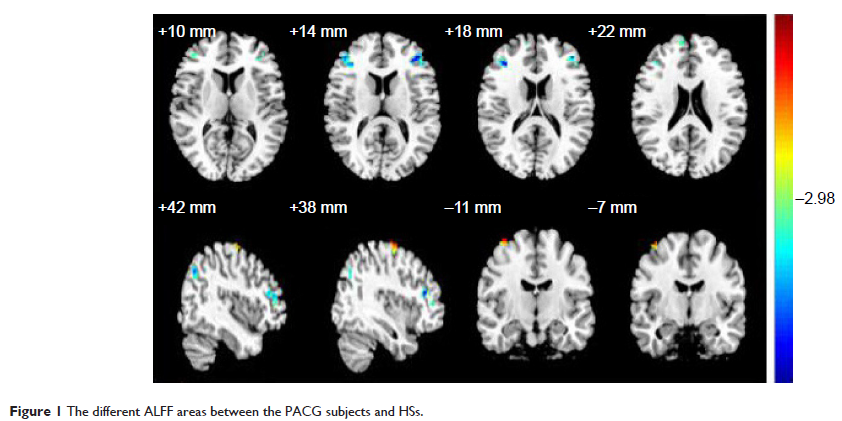
Methods: A total of twenty one patients with PACG (eight males and 13 females), and twenty one healthy subjects (nine males and twelve females) closely matched in age, sex, and education, each underwent a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging scan. The ALFF method was used to assess the local features of spontaneous brain activity. The correlation analysis was used to explore the relationships between the observed mean ALFF signal values of the different areas in PACG patients and the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL).
Results: Compared with the healthy subjects, patients with PACG had significant lower ALFF areas in the left precentral gyrus, bilateral middle frontal gyrus, bilateral superior frontal gyrus, right precuneus, and right angular gyrus, and higher areas in the right precentral gyrus. In the PACG group, there were significant negative correlations between the mean ALFF signal value of the right middle frontal gyrus and the left mean RNFL thickness (r =-0.487, P =0.033), and between the mean ALFF signal value of the left middle frontal gyrus and the right mean RNFL thickness (r =-0.504, P =0.020).
Conclusion: PACG mainly involved in the dysfunction in the frontal lobe, which may reflect the underlying pathologic mechanism of PACG.
Keywords: angle-closure glaucoma, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation, functional magnetic resonance imaging, resting state, spontaneous activity, retinal nerve fiber layer