108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

过敏原表位片段和 R848 的共同递送可通过诱导耐受性树突状细胞和调节性 T 细胞来抑制食物过敏
Authors Hong J, Xiao X, Gao Q, Li S, Jiang B, Sun X, Ran P, Yang P
Received 12 May 2019
Accepted for publication 29 July 2019
Published 30 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 7053—7064
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S215415
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Food allergy (FA) is a significant public health problem. The therapeutic efficacy for FA is unsatisfactory currently. The breakdown of intestinal immune tolerance is associated with the pathogenesis of FA. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop novel therapeutic methods to restore immune tolerance in treating FA.
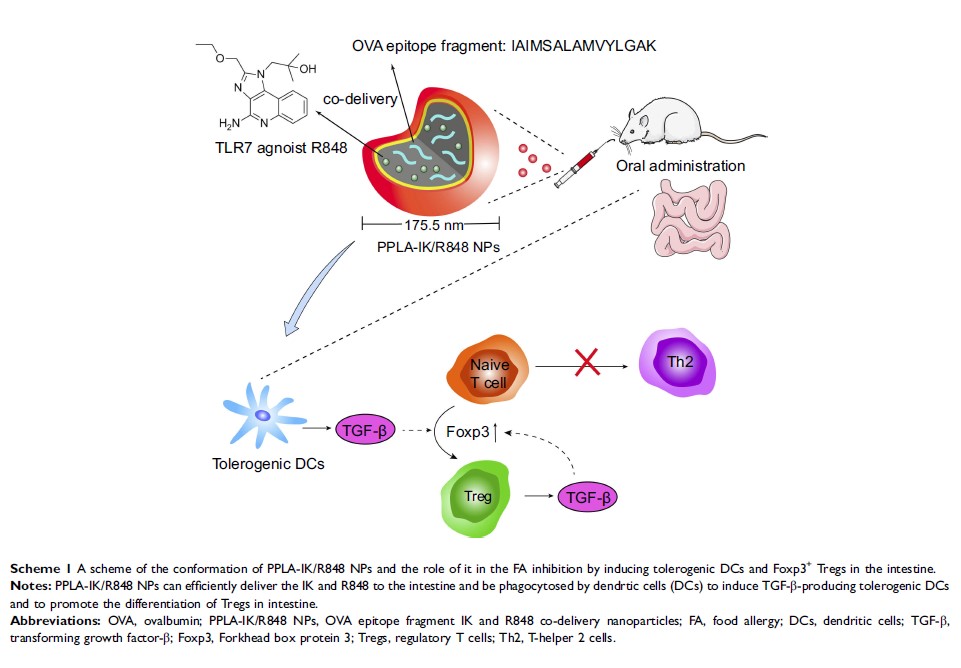
Methods: We proposed an oral administration strategy to treat FA by co-delivering food allergen epitope fragment (peptide: IK) and adjuvant R848 (TLR7 ligand) in the mPEG–PDLLA nanoparticles (PPLA-IK/R848 NPs). The generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells (DCs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs) induced by PPLA-IK/R848 NPs were evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The therapeutic effects of PPLA-IK/R848 NPs were also assessed in an OVA-induced FA model.
Results: PPLA-IK/R848 NPs could efficiently deliver IK to DCs to drive DCs into the tolerogenic phenotypes and promote the differentiation of Tregs in vitro and in vivo, significantly inhibited FA responses through the recovery of intestinal immune tolerance.
Conclusion: Oral administration of PPLA-IK/R848 NPs could efficiently deliver IK and R848 to intestinal DCs and stimulate DCs into allergen tolerogenic phenotype. These tolerogenic DCs could promote the differentiation of Tregs, which significantly protected mice from food allergic responses. This study provided an efficient formulation to alleviate FA through the recovery of immune tolerance.
Keywords: food allergy, co-delivery, allergen epitope fragment, R848, dendritic cells, Tregs