108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对细胞大小和类型有依赖性的细胞摄取、细胞毒性和金纳米颗粒体内分布
Authors Xia Q, Huang J, Feng Q, Chen X, Liu X, Li X, Zhang T, Xiao S, Li H, Zhong Z, Xiao K
Received 30 April 2019
Accepted for publication 6 August 2019
Published 28 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6957—6970
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S214008
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Melinda Thomas
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have shown great promise in biomedical applications. However, the interaction of AuNPs with biological systems, its underlying mechanisms and influencing factors need to be further elucidated.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to systematically investigate the effects of particle size on the uptake and cytotoxicity of AuNPs in normal cells and cancer cells as well as their biological distribution in vivo.
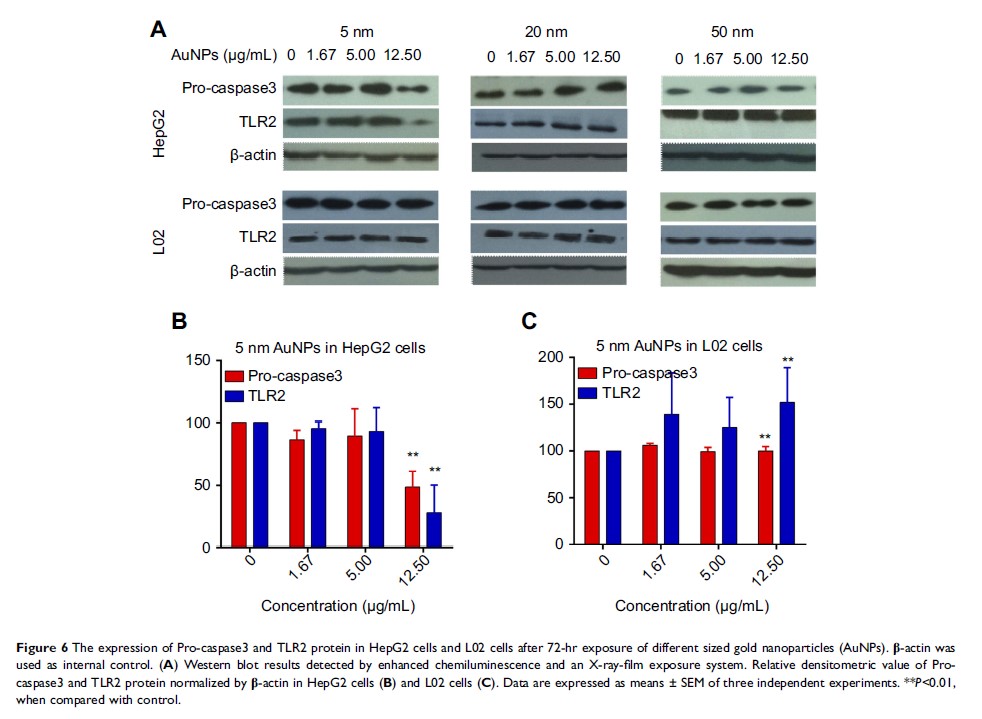
Results: Our data demonstrated that the uptake of AuNPs increased in HepG2 cancer cells but decreased in L02 normal cells, with the increase of particle size (5-50 nm). In both cancer cells and normal cells, small (5 nm) AuNPs exhibited greater cytotoxicity than large ones (20 and 50 nm). Interestingly, 5 nm AuNPs induced both apoptosis and necrosis in HepG2 cells through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the activation of pro-caspase3, whereas it mainly induced necrosis in L02 cells through the overexpression of TLR2 and the release of IL-6 and IL-1a cytokines. Among them, 50 nm AuNPs showed the longest blood circulation and highest distribution in liver and spleen, and the treatment of 5 nm AuNPs but not 20 nm and 50 nm AuNPs resulted in the increase of neutrophils and slight hepatotoxicity in mice.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the particle size of AuNPs and target cell type are critical determinants of cellular uptake, cytotoxicity and underlying mechanisms, and biological distribution in vivo, which deserves careful consideration in the future biomedical applications.
Keywords: gold nanoparticles, particle size, uptake, toxicity, biodistribution