108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

循环中 syndecan-1 作为一种新型生物标记物,与肺功能、全身性炎症和 COPD 恶化有关
Authors Li D, Wu Y, Guo S, Qin J, Feng M, An Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Xiong S, Zhou H, Zeng Q, Chen L, Wen F
Received 7 March 2019
Accepted for publication 12 July 2019
Published 28 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1933—1941
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S207855
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Chunxue Bai
Introduction: Patients with COPD often show increased systemic inflammation which is associated with lower functional status, greater exacerbation risk, and worse clinical outcomes. Syndecans (SDCs), a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs), have been found to involve in inflammatory processes in many chronic inflammatory diseases. The aim of this preliminary clinical study was to investigate the possible association between two SDCs, SDC-1 and SDC-4, with lung function, systemic inflammation, and risk of exacerbations in COPD patients.
Method: Serum SDC-1 and SDC-4 levels were measured in 101 COPD patients and 57 health controls. Correlations between SDCs and other parameters were analyzed using Spearsman’s rho. Receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the threshold value in differentiating disease status.
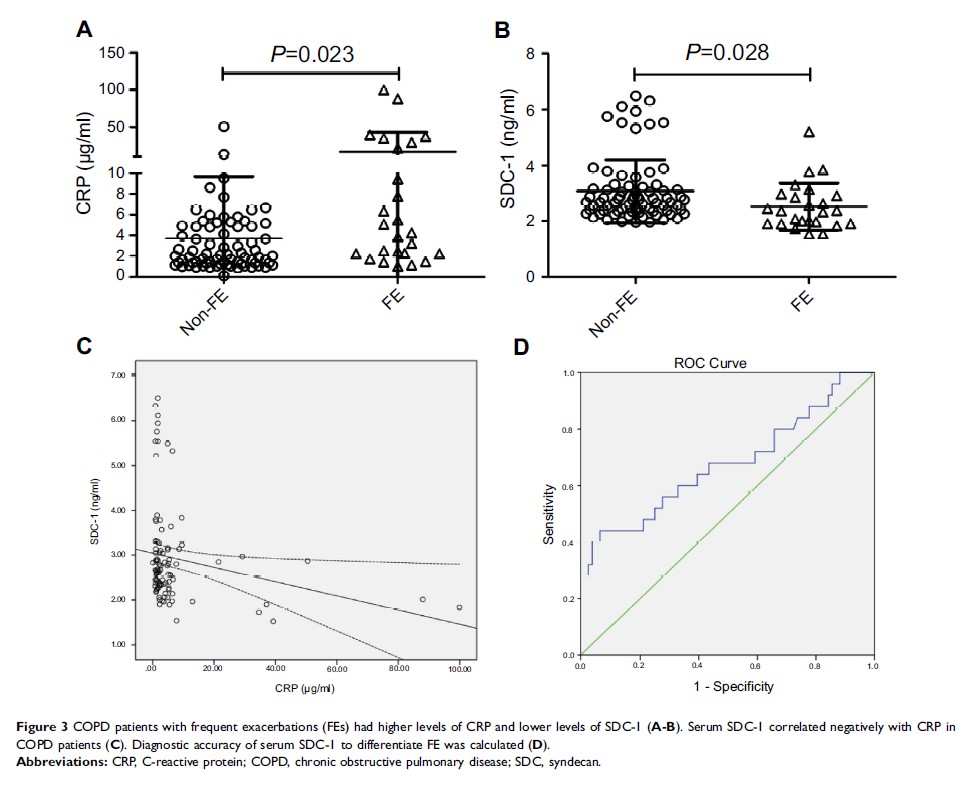
Results: Although both serum SDC-1 and SDC-4 showed a downward trend in COPD patients, only SDC-1 levels were correlated positively with the ratio of FEV1/FVC and parameters of small airway obstruction. Besides, SDC-1 but not SDC-4, was negatively correlated with C-reactive protein (CRP) in COPD patients and downregulated in frequent exacerbators (FEs) of COPD. Using a cutoff value of 2.08 ng/mL, the sensitivity and specificity of SDC-1 to differentiate FE were 44% and 93.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: In conclusion, circulating SDC-1 may be a novel inflammatory biomarker associated with lung function and systemic inflammation in patients with COPD, which could also be useful to identify the risk of COPD exacerbation. Further studies should be performed to clarify the influences of SDC-1 on the pathogenesis and outcomes of COPD.
Keywords: syndecan, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, systemic inflammation, exacerbation, biomarker