108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-1271 通过靶向卵巢癌细胞中的 ZEB1 抑制生长、侵袭和上皮-间质转化
Authors Jiao Y, Zhu G, Yu J, Li Y, Wu M, Zhao J, Tian X
Received 11 June 2019
Accepted for publication 8 August 2019
Published 28 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6973—6980
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S219018
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Objective: MicroRNA-1271 (miR-1271) has a role in suppressing cell growth, cell cycle and promoting cell apoptosis in many cancers. This research was to explore the great role of miR-1271 in ovarian cancer (OC).
Patients and Methods: RT-qPCR was utilized to evaluate the mRNA levels of miR-1271 and its target gene. The proliferative and invasive abilities were measured using Cell Counting Kit-8 and transwell assays. The overall survival rate of OC patients was assessed by Kaplan–Meier method.
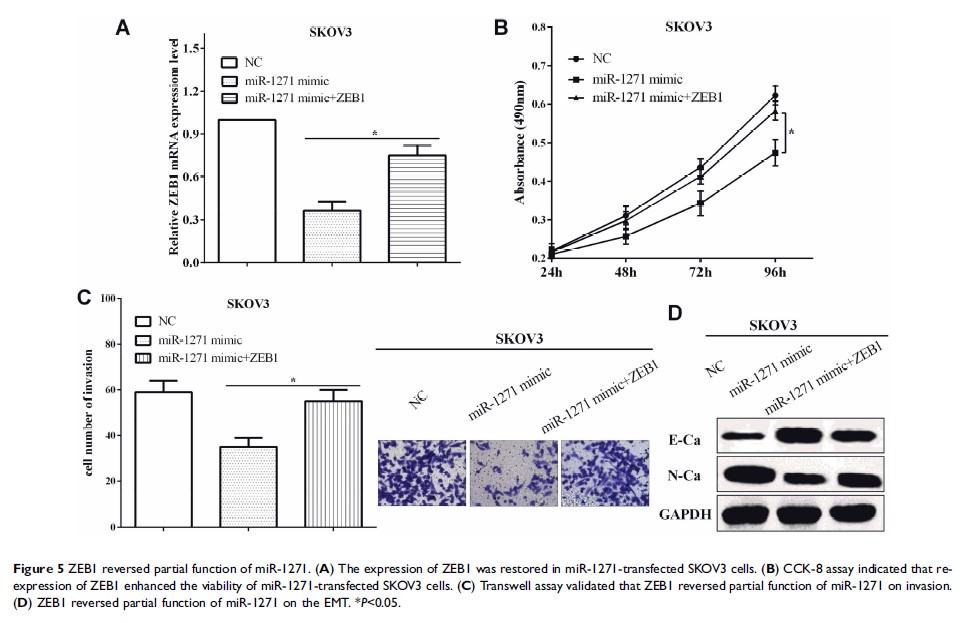
Results: miR-1271 was downregulated in OC tissues, and downregulation of miR-1271 predicted a poor outcome of the OC patients. Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) was a target gene of miR-1271 and its expression was regulated by miR-1271 in OC. The expression of miR-1271 had a negative connection with the expression of ZEB1 in OC tissues. miR-1271 inhibited cell viability and invasion-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition in SKOV3 cells. ZEB1 reversed partial roles of miR-1271 on viability and invasion in OC.
Conclusion: miR-1271 inhibited cell proliferation and invasion-mediated EMT in OC. The newly identified miR-1271/ZEB1 axis provides novel insight into the pathogenesis of OC.
Keywords: miR-1271, proliferation, invasion, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), ovarian cancer