109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
吴茱萸碱磷脂纳米复合物的纳米乳剂的吸收改善与体内动力学特点
Authors Hu J, Chen D, Jiang R, Tan Q, Zhu B, Zhang J
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 4411—4420
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S59812
Received 27 December 2013, Accepted 10 March 2014, Published 17 September 2014
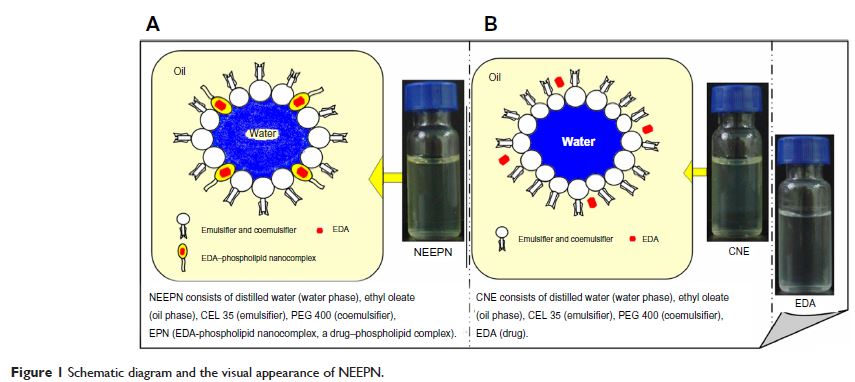
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess the improved absorption and in vivo kinetic characteristics of a novel water-in-oil nanoemulsion containing evodiamine–phospholipid nanocomplex (NEEPN) when administered orally.
Methods: NEEPN was fabricated by loading an evodiamine–phospholipid nanocomplex into a water-in-oil nanoemulsive system. The gastrointestinal absorption of NEEPN was investigated using an in situ perfusion method. The modified in vivo kinetic characteristics of evodiamine (EDA) in NEEPN were also evaluated.
Results: Compared with EDA or conventional nanoemulsions containing EDA instead of evodiamine–phospholipid complex, NEEPN with its favorable in vivo kinetic characteristics clearly enhanced the gastrointestinal absorption and oral bioavailability of EDA; for example, the relative bioavailability of NEEPN to free EDA was calculated to be 630.35%, and the effective permeability of NEEPN in the colon was 8.64-fold that of EDA.
Conclusion: NEEPN markedly improved the oral bioavailability of EDA, which was probably due to its increased gastrointestinal absorption. NEEPN also increased efficacy and reduced adverse effects for oral delivery of EDA. Such finding demonstrates great clinical significance as an ideal drug delivery system demands high efficacy and no adverse effects.
Keywords: nanoemulsive system, evodiamine–phospholipid, nanocomplexes, gastrointestinal absorption, oral bioavailability, water-in-oil
Methods: NEEPN was fabricated by loading an evodiamine–phospholipid nanocomplex into a water-in-oil nanoemulsive system. The gastrointestinal absorption of NEEPN was investigated using an in situ perfusion method. The modified in vivo kinetic characteristics of evodiamine (EDA) in NEEPN were also evaluated.
Results: Compared with EDA or conventional nanoemulsions containing EDA instead of evodiamine–phospholipid complex, NEEPN with its favorable in vivo kinetic characteristics clearly enhanced the gastrointestinal absorption and oral bioavailability of EDA; for example, the relative bioavailability of NEEPN to free EDA was calculated to be 630.35%, and the effective permeability of NEEPN in the colon was 8.64-fold that of EDA.
Conclusion: NEEPN markedly improved the oral bioavailability of EDA, which was probably due to its increased gastrointestinal absorption. NEEPN also increased efficacy and reduced adverse effects for oral delivery of EDA. Such finding demonstrates great clinical significance as an ideal drug delivery system demands high efficacy and no adverse effects.
Keywords: nanoemulsive system, evodiamine–phospholipid, nanocomplexes, gastrointestinal absorption, oral bioavailability, water-in-oil