108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

硫化砷诱导 miR-4665-3p 抑制胃癌细胞的侵袭和迁移
Authors Zhang X, Tan Z, Kang T, Zhu C, Chen S
Received 19 March 2019
Accepted for publication 6 June 2019
Published 26 August 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 3037—3049
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S209219
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
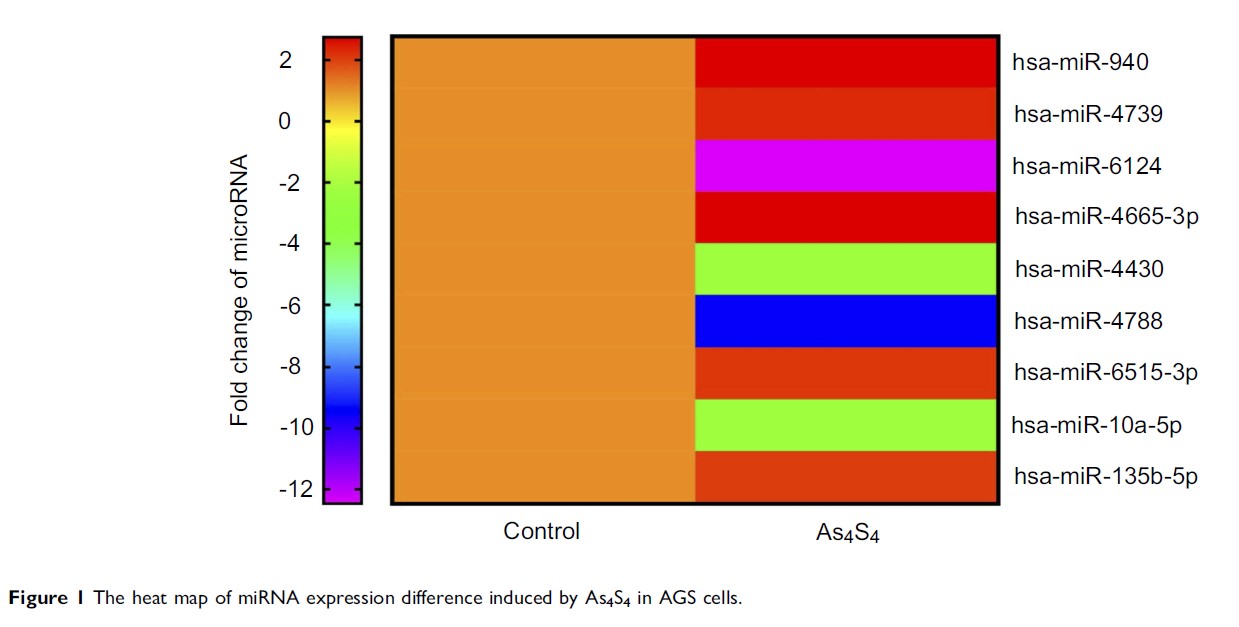
Purpose: Gastric carcinogenesis is a multistep process and is the second-highest cause of cancer death worldwide with a high incidence of invasion and metastasis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) engage in complex interactions with the machinery that controls the transcriptome and concurrently target multiple mRNAs. Recent evidence has shown that miRNAs are involved in the cancer progression, including promoting cell-cycle, conferring resistance to apoptosis, and enhancing invasiveness and metastasis. Here, we aim to elucidate the roles of miRNAs, especially microRNA-4665-3p (miR-4665-3p), in the inhibitory effect of arsenic sulfide in gastric cancer (GC).
Methods: The arsenic sulfide-induced miRNA expression alterations in AGS cells was determined by miRNA microarray. RT-PCR was used to further verify the arsenic sulfide-regulated miRNAs in GC tissues. The inhibition of miR-4665-3p on the migration and invasion of GC cells were determined by wound healing assay and transwell assay. Western blot analysis was used to detect the expression of EMT related proteins and the putative target of miR-4665-3p.
Results: The miR-4665-3p was up-regulated by arsenic sulfide and showed inhibition upon the migration and invasion of GC cells. MiRBase and Western blotting indicated that miR-4665-3p directly down-regulated the oncoprotein GSE1. Morphological observation also indicated that the up-regulation of miR-4665-3p inhibits the EMT in GC cells.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrates that the increased expression of miR-4665-3p induced by arsenic sulfide suppresses the cell invasion, metastasis and EMT of GC cells, and has the potential to be a novel therapeutic target in GC.
Keywords: arsenic sulfide, miR-4665-3p, gastric cancer, invasion, migration