108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-29a 通过靶向 SIRT1 在宫颈癌中发挥肿瘤抑制作用,并可预测患者预后
Authors Nan P, Niu Y, Wang X, Li Q
Received 2 June 2019
Accepted for publication 31 July 2019
Published 26 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6917—6925
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S218043
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Introduction: Cervical cancer is the second most frequently malignant tumors in females and metastasis is a challenge of the treatment of cervical cancer. MiR-29a is usually low expressed in several tumors and its functions in cervical cancer remain unclear.
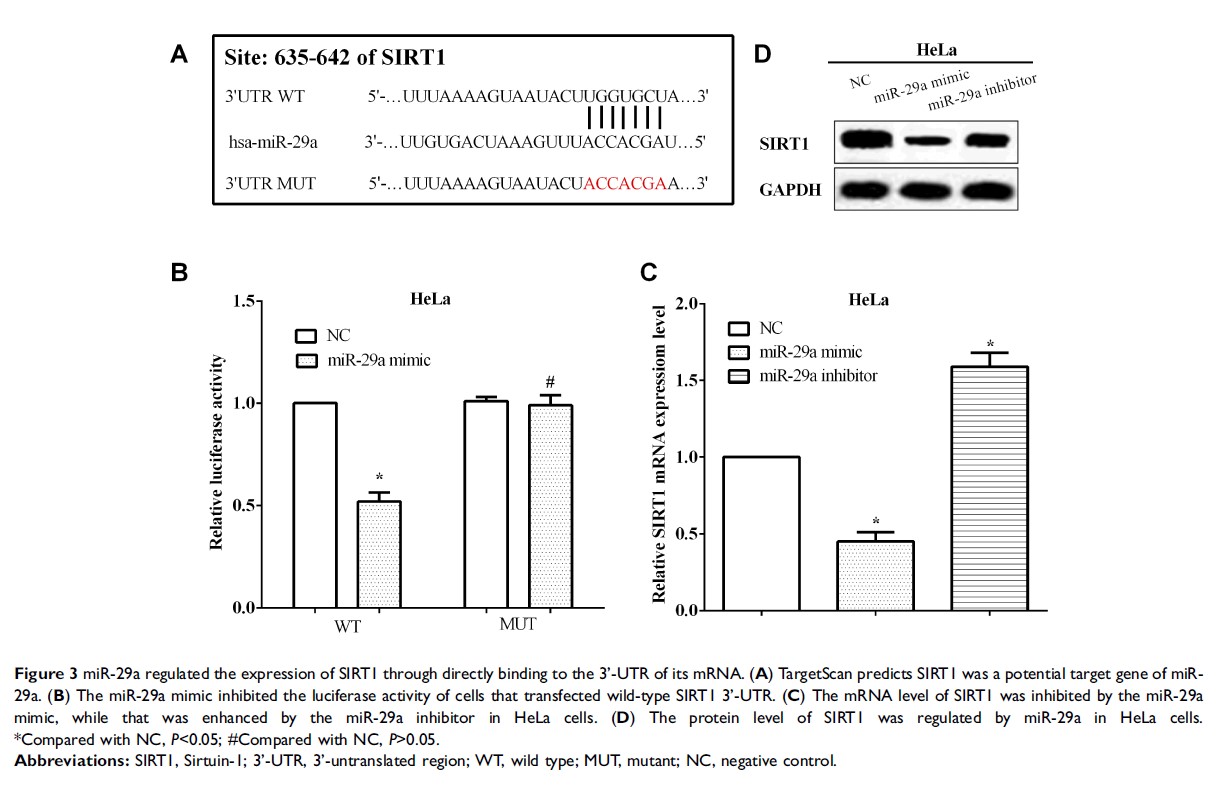
Patients and methods: The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was employed to assess the expression of miR-29a and the Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). Cell metastatic ability was assessed using Transwell and Western blot assays. The dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to verify that miR-29a targeted to the 3’-untranslated region (UTR) of SIRT1 mRNA.
Results: MiR-29a was low expressed in cervical cancer and downregulation of miR-29a was associated with poor outcome. MiR-29a regulated the expression of SIRT1 by targeting to its 3’-UTR of mRNA in HeLa cells. SIRT1 was upregulated in cervical cancer tissues and cells in comparison with the non-tumor tissues and normal cells. Upregulation of SIRT1 predicted worse outcome of cervical cancer patients. MiR-29a was participated in the migration, invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cervical cancer through directly targeting to the 3’-UTR of SIRT1 mRNA. SIRT1 reversed partial roles of miR-29a on metastasis in cervical cancer.
Conclusion: miR-29a suppressed migration, invasion and EMT by directly targeting to SIRT1 in cervical cancer. The newly identified miR-29a/SIRT1 axis provides novel insight into the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
Keywords: miR-29a, cervical cancer, SIRT1, tumor suppressor, EMT