108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一个探索淫羊藿活性化合物和药理作用机制的网络药理学方法,用于治疗卵巢早衰
Authors Zhao H, Shan Y, Ma Z, Yu M, Gong B
Received 12 March 2019
Accepted for publication 28 June 2019
Published 22 August 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 2997—3007
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S207823
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
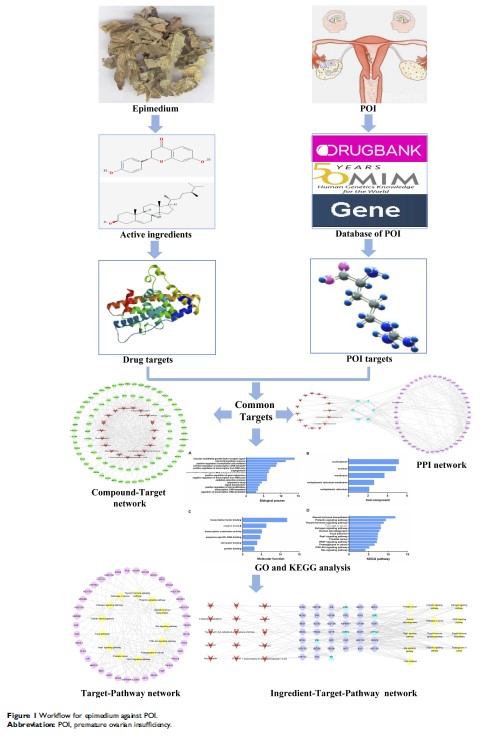
Background and purpose: Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) refers to a hypergonadotropic hypoestrogenism and the condition of pre-onset ovarian function failure. Epimedium is a common traditional Chinese herbal medicine that is widely used to relieve POI in China. To systematically explore the pharmacological mechanism of epimedium on POI therapy, a network pharmacology approach was conducted at the molecular level.
Methods: In this study, we adopt the network pharmacology method, which mainly includes active ingredients prescreening, target prediction, gene enrichment analysis and network analysis.
Results: The network analysis revealed that 6 targets (ESR1, AR, ESR2, KDR, CYP19A1 and ESRRG) might be the therapeutic targets of epimedium on POI. In addition, gene-enrichment analysis suggested that epimedium appeared to play a role in POI by modulating 6 molecular functions, 5 cellular components, 15 biological processes and striking 52 potential targets involved in 13 signaling pathways.
Conclusion: This study predicted the pharmacological and molecular mechanism of epimedium against POI from a holistic perspective, as well as provided a powerful tool for exploring pharmacological mechanisms and rational clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: network pharmacology, premature ovarian insufficiency, epimedium, infertility, GO, KEGG