109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
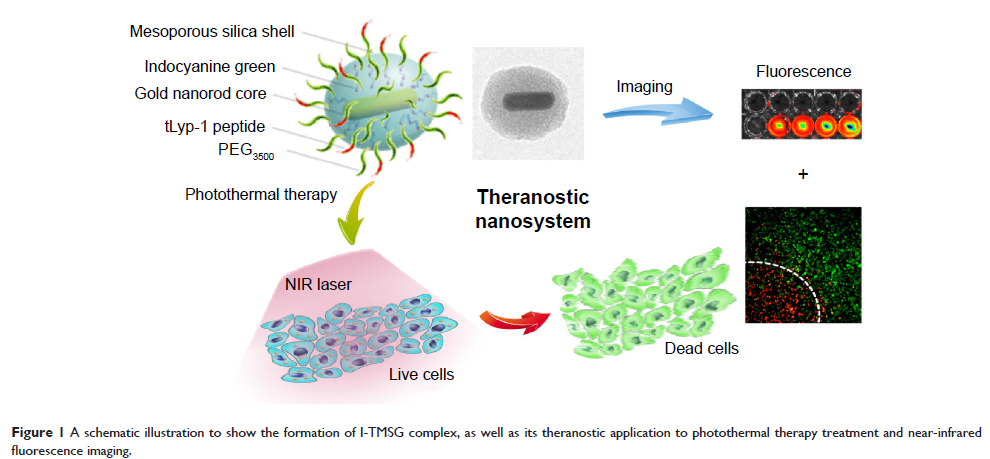
金纳米棒/孔二氧化硅基纳米复合材料作为治疗诊断试剂,可用于近红外影像和激光诱导的光热治疗技术
Authors Liu Y, Xu M, Chen Q, Guan G, Hu W, Zhao X, Qiao M, Hu H, Liang Y, Zhu H, Chen D
Published Date July 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 4747—4761
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S82940
Received 15 February 2015, Accepted 6 April 2015, Published 28 July 2015
Approved for publication by Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Photothermal therapy (PTT) is widely regarded as a promising technology for cancer treatment. Gold nanorods (GNRs), as excellent PTT agent candidates, have shown high-performance photothermal conversion ability under laser irradiation, yet two major obstacles to their clinical application are the lack of selective accumulation in the target site following systemic administration and the greatly reduced photothermal conversion efficiency caused by self-aggregating in aqueous environment. Herein, we demonstrate that tLyp-1 peptide-functionalized, indocyanine green (ICG)-containing mesoporous silica-coated GNRs (I-TMSG) possessed dual-function as tumor cells-targeting near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent probe and PTT agents. The construction of the nanostructure began with synthesis of GNRs by seed-mediated growth method, followed by the coating of mesoporous silica, the chemical conjugation of PEG and tLyp-1 peptide, and the enclosure of ICG as an NIR imaging agent in the mesoporous. The as-prepared nanoparticles could shield the GNRs against their self-aggregation, improve the stability of ICG, and exhibit negligible dark cytotoxicity. More importantly, such a theranostic nanocomposite could realize the combination of GNRs-based photothermal ablation under NIR illumination, ICG-mediated fluorescent imaging, and tLyp-1-enabled more easy endocytosis into breast cancer cells. All in all, I-TMSG nanoparticles, in our opinion, possessed the strong potential to realize the effective diagnosis and PTT treatment of human mammary cancer.
Keywords: theranostic nanoagents, photothermal therapy, indocyanine green, gold nanorods, mesoporous silica, anti-mammary cancer