108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-671-5p 的过表达显示结肠癌预后不良,加速结肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Jin W, Shi J, Liu M
Received 13 June 2019
Accepted for publication 9 August 2019
Published 22 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6865—6873
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S219421
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Purpose: Colon cancer is one of the common malignancies worldwide, and many genes, including microRNAs (miRNAs), have been demonstrated that associated with progression of various diseases, including cancers. The aim of this study is to investigate the potential role of miR-671-5p in colon cancer.
Patients and methods: Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to detect the expression levels of miR-671-5p in 115 paired colon cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues, as well as in colon cancer cells. Kaplan-Meier curve and Cox regression analyses were used to estimate the prognostic significance of miR-671-5p in colon cancer. CCK-8 assay, colony-formation assay, Transwell migration and invasion assays were used to evaluate the effects of miR-671-5p on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in colon cancer.
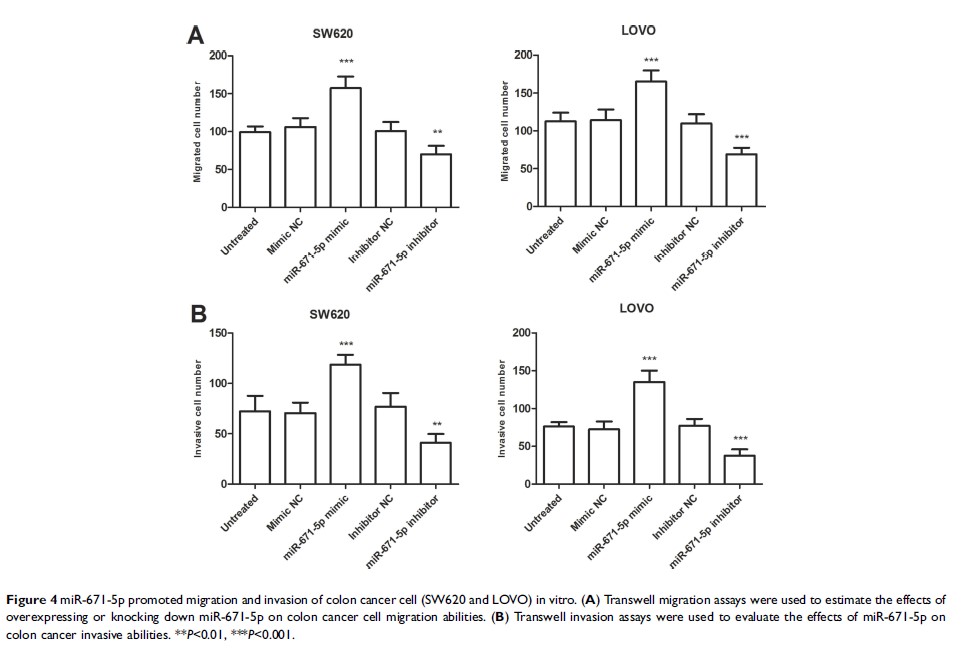
Results: We found that miR-671-5p expression was increased in colon cancer tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of miR-671-5p was found associated with lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, and poor overall survival of patients with colon cancer. By exploiting miR-671-5p mimics and inhibitors, miR-671-5p overexpression significantly increased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while downregulation of miR-671-5p inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, miR-671-5p may act as an oncogene in colon cancer and promote proliferation, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells by targeting TRIM67. And it may be a promising prognostic biomarker and therapeutic application for colon cancer treatment.
Keywords: miR-671-5p, colon cancer, prognosis, proliferation, migration, invasion