108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CITED1 通过 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路促进乳头状甲状腺癌的进展
Authors Wang Y, Huang H, Hu F, Li J, Zhang L, Pang H
Received 8 May 2019
Accepted for publication 26 July 2019
Published 21 August 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 6769—6777
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S215025
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: The incidence rate of thyroid cancer, the most common endocrine malignancy, has increased rapidly over the past 10 years. However, the fundamental molecular mechanisms underlying the malignant progression of thyroid cancer are unclear.
Materials and methods: Firstly, quantitative real-time PCR analysis and Western blot analysis were used to investigate the expression of Cbp/p300 interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp rich carboxy-terminal domain 1 (CITED1) in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) cell lines. Then, we investigated the effects of CITED1 knockdown on cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion in in vitro and in vivo models of PTC.
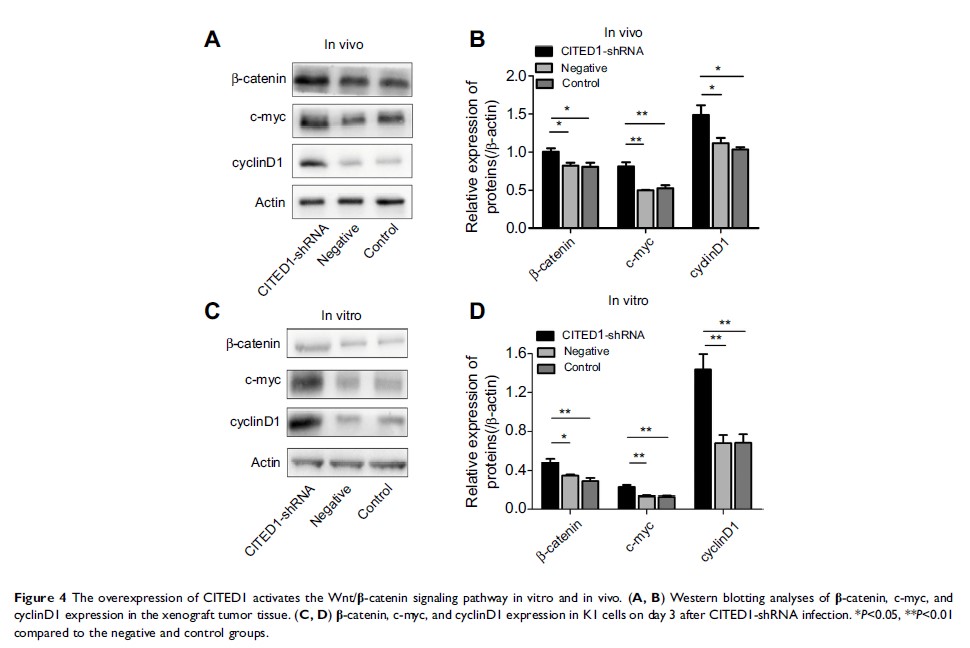
Results: CITED1 was upregulated in PTC cell lines, and CITED1 knockdown significantly suppressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion of K1 cells resulting in a G0/G1 phase block. Furthermore, the silencing of CITED1 significantly promoted cell apoptosis. In the in vivo study, the growth speed and weight of the transplanted tumor were significantly suppressed in nude mice infected with short hairpin RNA targeting CITED1 (CITE1-shRNA) cells. Furthermore, we found that CITED1-shRNA activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling in PTC.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings suggest that CITED1 knockdown facilitates apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and invasion in K1 cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: papillary thyroid carcinoma, CITED1, proliferation, invasion, Wnt/β-catenin signalling